A voltage regulator is an important component of your car's charging system. As the name indicates, it regulates the amount of voltage produced from the alternator to ensure a consistent voltage to the battery and electrical equipment in your car. The voltage from your alternator increases and decreases according to the speed the alternator rotates; too much voltage and your fuses blow, if you don’t have a regulator. Most new alternators have internal voltage regulators, meaning wiring is not necessary, but if you have an external regulator then you need to hook it up to the alternator and ignition system.
Open the hood of your car. Ensure the engine is cool before wiring the alternator voltage regulator.
Remove the black battery cable from the car’s battery terminal using a wrench. Remove the red battery cable using the same method.
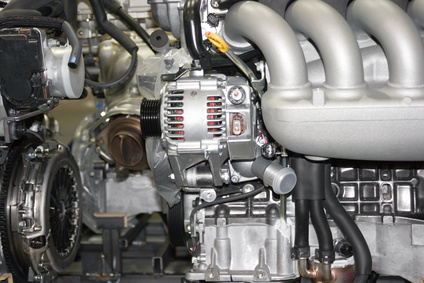
Locate the voltage regulator. It’s usually positioned above, or on the side of the alternator. It has a single rectangular plastic socket on the back which a plug containing four wires goes into.
Find the multi-wired harness nearby the alternator and voltage regulator. On the end of the harness is a plastic rectangular plug that has four colored wires attached. The brown wire goes to the ignition, the blue is the field wire and goes to the alternator, the red wire is the positive battery sensor and the white wire goes to alternator stator.
Insert the plug into the socket on the voltage regulator. It can only be inserted one way so you can’t get it wrong.
Reconnect the red battery cable to the positive battery terminal labeled “Pos.” Reconnect the black battery cable to the negative battery terminal labeled “Neg.” Close the hood of your car.