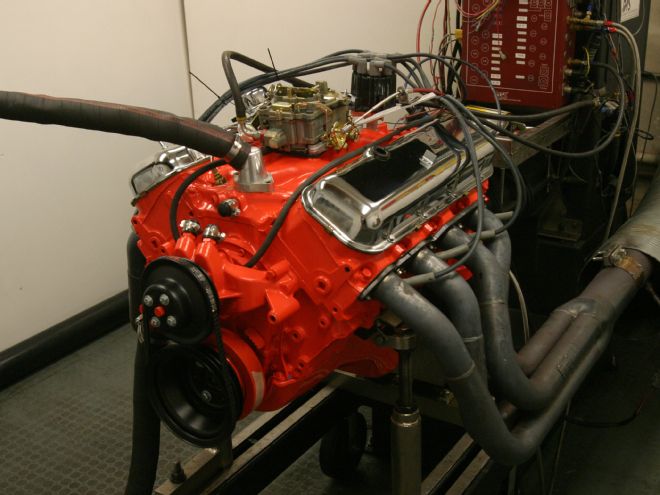

Like the rest of our Basket Case 1970 Chevrolet Chevelle project, we received the powerplant, a Chevy 396 big-block, disassembled in a crate. The engine was mocked together in the box, with the internals piled at the bottom. The box's contents revealed the parts we were dealing with, offered clues to the engine's history, and set the direction for the project in terms of what would be needed to revive the engine. The goal was a reliable resto-style build with good street manners and a healthy power increase over stock.
The Parts Pile
Typically the best scenario in an engine restoration is starting with a virgin engine core, one that is untouched since the day it was assembled by the factory. We weren't so lucky with our 396. The engine was wearing a fairly new coat of bright Chevy Orange paint and was simply mock-assembled in the crate. Obviously this thing had seen many hands in the past. Unlike an OE assembled engine, where you can be pretty sure that the components left the factory together, our mongrel box of parts could contain a little of everything (further inspection proved that it did).
Most engine components are marked with codes and casting numbers that can provide wide ranging information about the assembly as a whole and the individual components. Checking the numbers, our intake manifold, carb, and heads were all correct 1970 L34 396 components. We noted that our block carried a casting number of 3916323, indicating a 1968 block. However, the stamped code "ED" at the front of the block is for a 1966 Chevelle 325hp 396. Obviously the application cannot predate the casting of the block, so this unit must have been restamped somewhere along the way. Neither the casting number nor the stamping was correct for a 1970 SS396. Inspecting further, we found that the block was already bored 0.060 over and the cylinders well worn. To make matters worse, the main caps were a mismatched set.
The goal was a reliable resto-style build, with good street manners and a healthy power increase
While there was nothing unusual in the piston/rods/cylinder bore department, we did note that the replacement bearings in the rods were marked 0.030, indicating that the OE forged crank was likely reground more than once, and at the end of its service life. The crank numbers matched that of the block, with a 1968 manufacturing code, and proved to be 0.020 inch undersized at the main bearings. With another regrind needed to the well-worn journals we would most likely look to replace the crankshaft. Things were not off to a good start for our planned resto-build.
What to Do?
Our 396 core was essentially a hodgepodge of worn-out and mismatched parts, probably traded from one restoration shop to another over the years. Was it junk? For the intended use in a 1970 Chevelle restoration, it was. With numerous problems to work through, and since it had the wrong casting number for the application, it is just not the right starting point for this build. We put in a call to AA-Midwest, a large nationwide supplier of engine cores. As luck would have it, the company's inventory turned up the correct casting number 3969854 block, still in the standard dimensions.
Since the crank also needed replacement, the opportunity was open to add to the engine's displacement with an increase in stroke. Here a 4.00-inch-stroke forged crank from Eagle would replace the 3.75-inch-stroke stocker. The increase in stroke, combined with bores machined to 4.155 inches, yields a displacement of 434 ci, a healthy increase in engine size. Along with the crank, a new set of bulletproof Eagle H-beam rods offers a substantial increase in strength. A set of custom CP forged pistons was ordered to complete the internal package. The pistons actually represent a major step towards increased power, as they are built to work with CP's very low-friction 1.2/1.2/3mm metric ring package. These rings, which feature nitrided steel top rings, represent state-of-the-art compression sealing while cutting down tremendously on friction and heat compared to the factory 5/64-5/64-3/16 ring package.
Our 396 core was essentially a hodgepodge of worn-out and mismatched parts
With the bottom-end improvements setting the foundation for a meaningful increase in power, we moved our attention to the cylinder heads. Here, a set of aftermarket aluminum heads would be the easy choice for a performance build. However, we were approaching this project with restoration in mind and were determined to retain the production number 3931063 iron oval-port cylinder heads. We took liberties in the rebuilding of the heads, starting with an increase in valve size. We went from the production 2.06/1.72-inch valve diameter specification to a 2.19/1.88-inch combination. We also replaced the guides, not only to refresh the surface but to reduce the valve stem diameter from the factory spec of 3/8 inch to 11/32. This reduces the valve weight, improving the rpm capabilities of the valvetrain. The valve seats were machined to accept the larger valves using Serdi cutting equipment, which produces a high-flowing multi-angle seat form. Finally, the port bowls were hand-ported to blend the machine work to the existing ports, providing a significant increase in cylinder head flow (see flow table).
Given the added cubes and much improved cylinder heads, we were well on our way to substantially more than the 396's factory 350hp rating. The next items on the agenda were the camshaft and valvetrain. Here we opted for a hydraulic roller, both for the reliability and the chance for even greater power. Although bigger generally equates to more horsepower when it comes to camshaft selection, we were determined to keep the camshaft specifications modest in an effort to retain the factory engine's idle characteristics and running temperament. We did not want this resto engine to lope like a drag car. We had Competition Cams grind a custom single-pattern hydraulic retrofit roller cam with 224 degrees duration at 0.050, 0.566-inch lift, and a lobe separation angle of 112 degrees. The moderate duration and relatively wide lobe separation help tame the idle, while the substantial increase in lift from the factory 0.461/0.480-inch definitely helps the airflow. Along with the camshaft, a set of Comp retrofit hydraulic roller lifters, Comp pushrods, and Comp Magnum rocker arms complete the valvetrain package.
To complete the engine assembly, we were obligated to reuse the iron intake manifold and Quadrajet carburetor. Although an aftermarket intake could have offered a power improvement, we had the correct factory pieces and would not compromise on originality here. We had the Q-jet carburetor completely restored by Jet Performance, and in testing it proved to work as great as it looked. We did elect to upgrade the factory points-type distributor to a new PerTronix electronic unit, weighing the added reliability and the elimination of maintenance ahead of strict originality. Trans-Dapt was our main source for a variety of reproduction metal, including an OE-style oil pan, timing cover and pointer, chrome valve covers, and all of the miscellaneous fasteners, breathers, grommets, and small parts. Trans-Dapt offers a very wide range of products in both custom and OE replacement-style parts, and it was a big help in replacing the rusted, dented, and missing items we needed to finish off our engine.
To the Dyno!
To ensure that our engine assembly was ready for installation and to validate our power plan, a dyno test was the natural conclusion of the build. The time to find and correct any potential problems is before the engine is installed in the car. We certainly strayed from the strict restoration route in building this engine, although the external appearance offers little to give away the power hidden within. We expected strong performance from this "396."
We loaded the Chevy big-block onto a DTS engine dyno. Excitement was high as it fired to life for the first time. Before any power testing, we ran the engine through a 20-minute break-in cycle, after ensuring that the ignition timing and mixture were within running specs. The engine definitely delivered a performance sound, but the mild cam timing was apparent with a solid 14.7 in-hg of manifold vacuum showing at idle. That number showed us that this was going to be a well-behaved beast running on the street.
That number showed us that this was going to be a well-behaved beast running on the street
With the preliminary running out of the way, it was time to perform serious wide-open power testing. We began by working the engine in steps at ever-increasing rpm points to get a reading on fuel delivery via the air/fuel mixture readout. Right up the rpm range, the Jet Performance Quadrajet delivered lambda numbers that were right in line with the engine requirements. No additional calibration to the carburetor was required. We could already see from the power numbers registered that this was going to be a seriously hot street 'plant.
Next we dove into power pulls—and power the engine delivered! The longer stroke combination twisted torque in abundance, showing more than 550 lb-ft at 3,500 rpm. The indicated torque definitely showed staying power, holding over 500 lb-ft to the 5,400 rpm mark. This thing was strong. Looking at the horsepower side of the dyno results, the engine crested the 500hp mark by 4,900 rpm, on its way to a peak of 514 at 5,700. In testing, the engine pulled strongly to a full 6,000 rpm, with power holding very close to the peak recorded number. In the street rpm range, this modified yet stock-looking 396 was dishing out incredible grunt. With carefully selected modifications, our L34 big-block was 164 hp stronger than its stock gross power rating while looking and sounding for all the world like a factory piece. That fulfilled our objective perfectly.
Cylinder Head Flow Results
Big-Block Chevy No. 3931063 Oval Ports
2.06/1.72-Inch Valves vs. 2.19/1.88-Inch
SuperFlow 600 Flowbench
Tested at 28 Inches Water Depression
Vital Specs
Resto 396/434 Chevy Big-Block
Dyno Results
396/434 Chevy Big-Block
DTS Engine Dyno
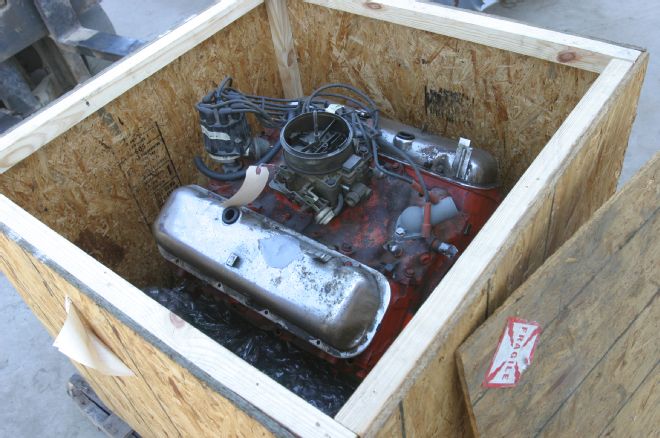

1 When we received our 396 engine for our Basket Case Chevelle, all was not well. The engine was mocked up in the crate, with the internal parts removed. Much of what we found was both worn out and incorrect, but at least we had the correct heads and induction system.
2 Inspecting the crankshaft, we found that the journals had been machined to their minimums and were once again worn out. This 3.750-inch stroke crank would be replaced with a new 4.00-inch stroke piece from Eagle.
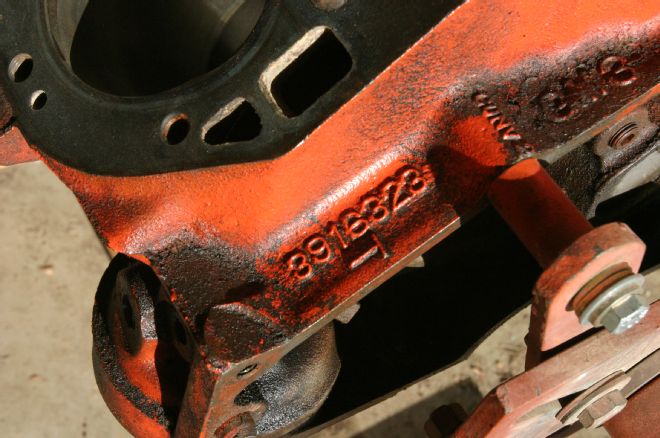

3 The casting number on the block was for a 1968 application, conspicuously incorrect for a 1970 Chevelle restoration. Because of the worn bores and mismatched main caps, we would be seeking another block.
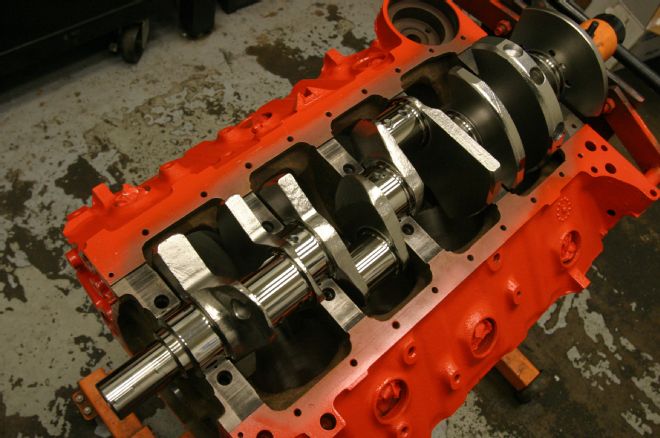

4 The solution was a casting-number-correct block core from AA-Midwest, which we had fully machined to 0.030 inch oversize (from 402 specs), line-honed, and decked. With the Eagle 4.00-inch stroke crank, our 396 was now a 434.
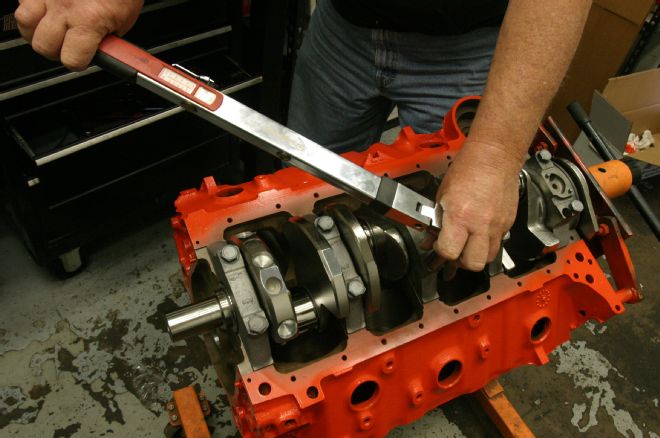

5 The crank was installed with Mahle/Clevite bearings and secured by the factory main caps and OE replacement fasteners.

6 The pistons and rods offer a ready opportunity for upgrade. The pistons are custom CP units, domed to deliver a compression ratio of 10.5:1 with our 101cc factory oval-port heads. Rods are Eagle H-beams, offering a considerable strength increase compared to the factory rods.
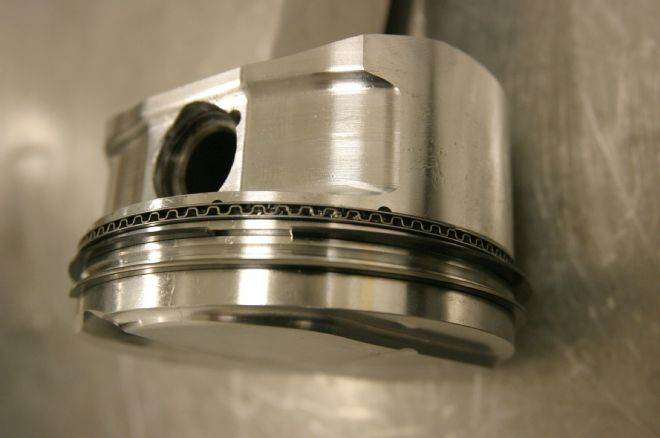

7 A major friction reduction in the bottom end was achieved with CP's low-drag metric ring package. With 1.2mm compression rings and a 3mm oil ring assembly, their rotating fiction is a fraction of the original 5/64-5/64-3/16 setup.
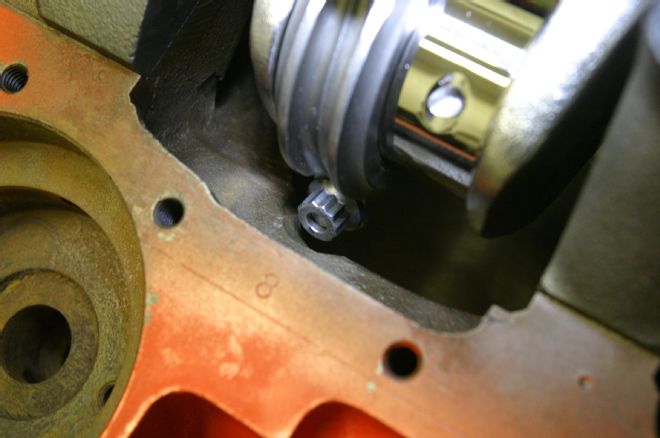

8 To clear the stroker bottom-end assembly, the bottoms of the cylinder bores required notches for rod bolt clearance. The notch here was minimal, thanks to the compact capscrew arrangement of the Eagle rods.
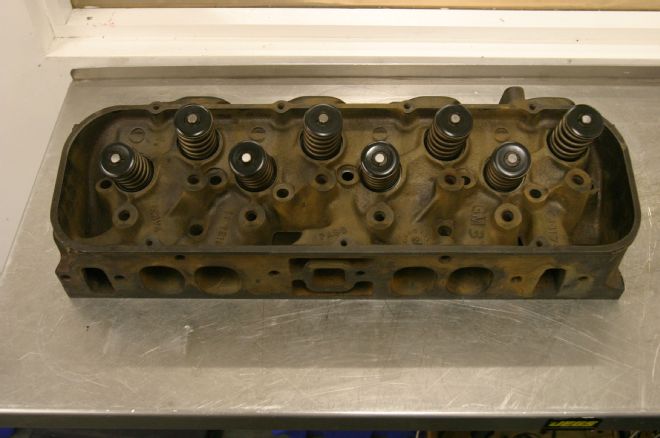

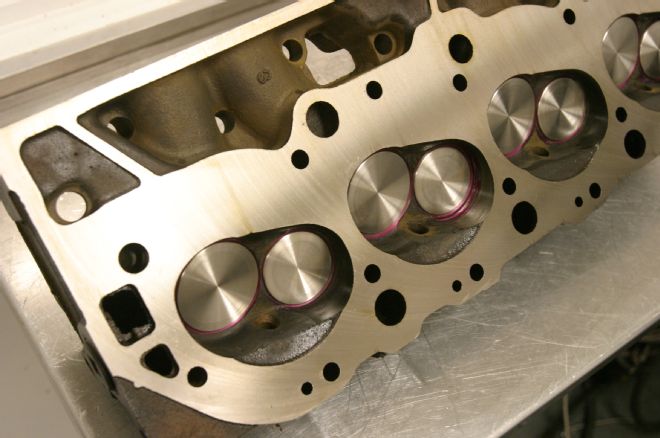
9 In the name of retaining an original outward appearance, the factory cylinder head castings were retained. Although these oval-port heads were no match in production form to their rectangular port brethren, in modified form they can satisfy the needs of the mightiest street 396.
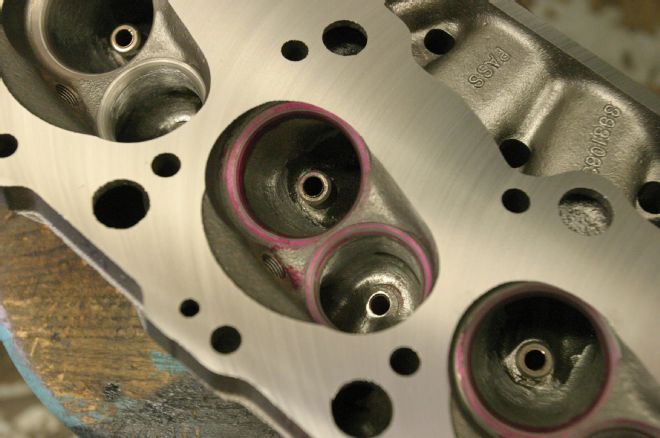

10 The heads were modified for oversized valves, with a true high-performance valve job and deep hand-porting of the port bowls.

11 Valve size was substantially increased from the production spec of 2.06/1.72 inches to 2.19/1.88 inches. Intake port flow of the modified castings showed 292 cfm, up from the factory 264 cfm.
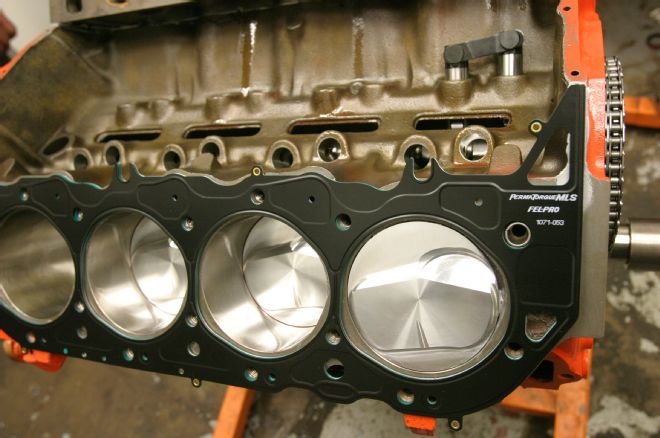

12 We employed modern gasket technology by using Fel-Pro multilayered steel head gaskets to seal the heads to the block. When using MLS gaskets, the surface finish of both the block and the cylinder head is specific to this gasket type.
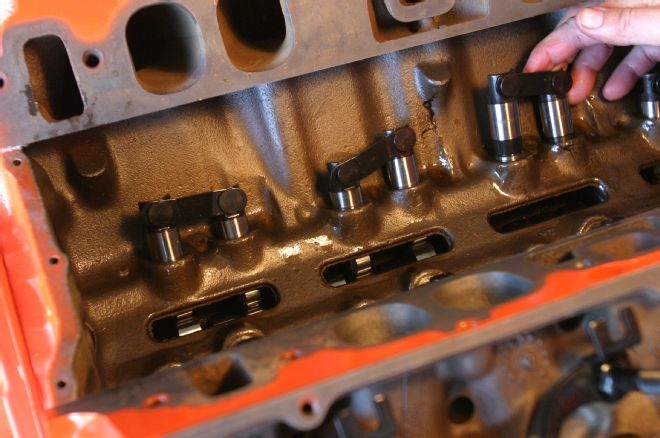

13 A custom Comp 224/0.566 retrofit hydraulic roller takes the place of the production flat-tappet cam. The roller virtually eliminates the chance of wiping a cam lobe and offers an increase in lift, adding to the engine's power potential.

14 A Comp billet timing set ensures long life and accurate cam timing. Note the thrust button required with a roller cam. We installed the cam at an intake centerline of 106 degrees.
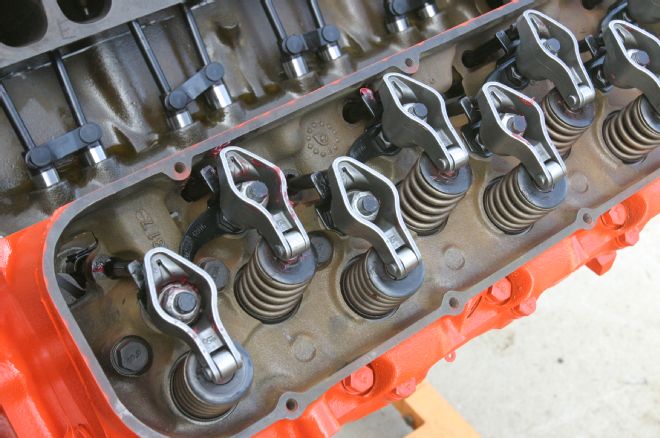

15 Comp also provided the full valvetrain, including the pushrods, guide plates, studs, and Magnum rockers.
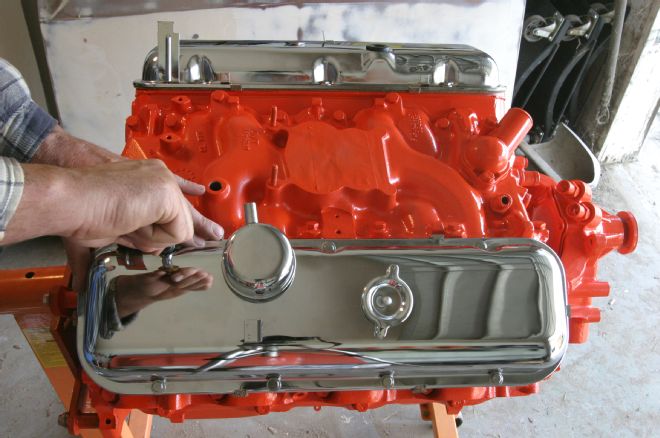

16 The factory Quadrajet intake manifold was a requirement, in keeping with our stock-appearing goals. For engine dress parts, we dove into the Trans-Dapt catalog, finding among the many offerings replacement sheetmetal for the oil pan, timing cover, and valve covers.
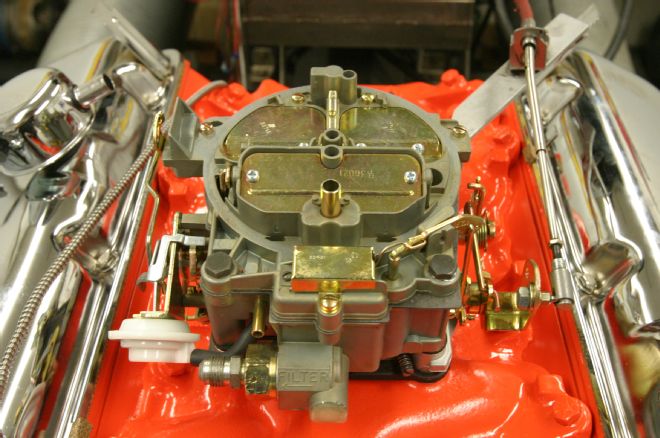

17 Our factory 1970 396 Quadrajet carburetor was fully rebuilt, restored, and calibrated for our engine combination by Jet Performance. It performed perfectly, requiring no subsequent changes to the calibration.

18 With 514 hp on tap, a 6,000 rpm powerband, and a mild factory appearance, our 396 project hit the bull's-eye in meeting our "look stock, go fast" goals.