As hot rodders, we tend to worry most about changes that make our pursuit of power harder or more expensive. That’s totally justifiable; new technology often brings both complication and a higher price. But just like the overhead valve configuration brought us more power than the flathead ever could, gasoline direct injection is the latest frontier in the search for cleaner emissions, more miles per gallon, and even higher power levels. We should be clear, though: it’s really those first two that are fueling Detroit’s research, but horsepower is definitely coming along for the ride. hChristopher Campbell
 Direct injection looks like multi-port EFI, but runs at about 40 times more pressure. The low-pressure line is fed 60 psi fuel from the in-tank electric lift pump, is then compressed by the injection pump, and sent to the fuel rails and injectors.
Direct injection looks like multi-port EFI, but runs at about 40 times more pressure. The low-pressure line is fed 60 psi fuel from the in-tank electric lift pump, is then compressed by the injection pump, and sent to the fuel rails and injectors.
Direct injection follows the same progression, except that fuel is sprayed directly into the cylinders. Sounds like a very minor change that makes sense: send the fuel directly where it needs to be anyways, but there’s more to it.
While about 60 psi at the injector is common on gasoline PFI systems, gasoline DI systems require injector pressures of more than 1,000 psi. That in turn requires a completely different injector design since it controls such high fuel pressure and the nozzle must withstand the violence within the combustion chamber. A much more powerful pump is required to generate that fuel pressure, so the electric in-tank pump now serves merely to lift the fuel up to a mechanical injection pump driven off the front of the cam, supplying the full fuel pressure to the injectors.
Further detonation resistance comes from rapid combustion, which occurs because of the unique piston design in a DI engine; typically, it has a bowl to direct fuel spray toward the spark plug. This makes the area near the plug slightly richer, improving cold-start emissions (a current issue with PFI), and creates a more vigorous flame. Speaking of cranking, by injecting fuel directly into the cylinder during the start phase, the engine hits idle rpm as much as 50 percent quicker, creating even less start-up related emissions.
That same technology has led to a sort of micro-hybrid start-stop technology that companies like Bosch are developing, which require no starter motor. By stopping the engine with the piston in the optimum position, the engine can be restarted in a fraction of a second by injecting fuel and igniting the plugs in the firing sequence until idle speed is reached. In other applications, a small battery is used in conjunction to get things going, such as on the 2014 Chevy Malibu. It’s not far fetched that we’ll be seeing this on performance cars in the future.
 The C7.R will be running its own specifically suited version of the DI controlled LT1 in competition. This won’t be new ground since Chevrolet has previously raced DI in C5.R and C6.R Corvettes with great success. The difference is that what they learn will directly transfer to hot rodders looking to prep their own C7s for track use.
The C7.R will be running its own specifically suited version of the DI controlled LT1 in competition. This won’t be new ground since Chevrolet has previously raced DI in C5.R and C6.R Corvettes with great success. The difference is that what they learn will directly transfer to hot rodders looking to prep their own C7s for track use.
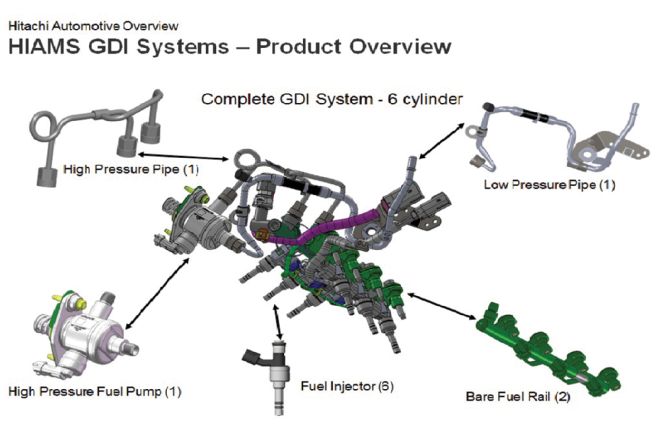 The specifics of the IndyCar engine’s DI system are a tightly guarded secret and photography is not allowed, but on a fundamental level, it is similar in design and operations to the V6 system developed by Hitachi shown here.
The specifics of the IndyCar engine’s DI system are a tightly guarded secret and photography is not allowed, but on a fundamental level, it is similar in design and operations to the V6 system developed by Hitachi shown here.
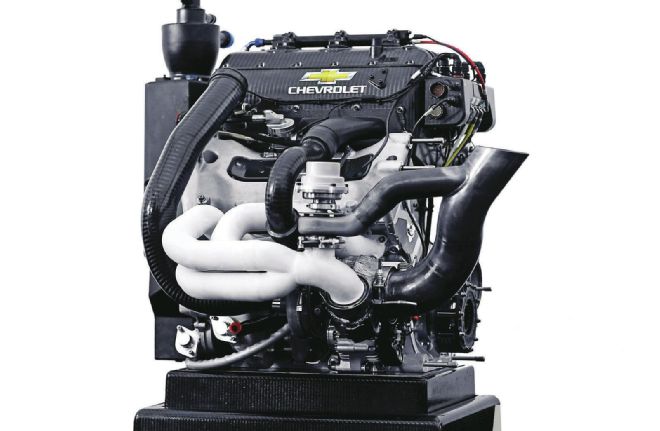 It’s not often that an engine rewrites the rules of a race series, but when Chevrolet introduced its 2.2L twin-turbo V6 for the company’s return to IndyCar, it took exactly one season for the rules committee to require a spec twin-turbo system to level the playing field for the far outclassed single-turbo Honda system. GM embedded top engineers with Ilmor Engineering (UK) to develop and manufacture race components and create the engine calibration. The cars are assembled and tested in the U.S. GM partnered with Hitachi to create the DI system, which we’re told is based on production components.
It’s not often that an engine rewrites the rules of a race series, but when Chevrolet introduced its 2.2L twin-turbo V6 for the company’s return to IndyCar, it took exactly one season for the rules committee to require a spec twin-turbo system to level the playing field for the far outclassed single-turbo Honda system. GM embedded top engineers with Ilmor Engineering (UK) to develop and manufacture race components and create the engine calibration. The cars are assembled and tested in the U.S. GM partnered with Hitachi to create the DI system, which we’re told is based on production components.
The real takeaway from the Chevy IndyCar engine success may be the way it uses DI and PFI on the same engine. The Hitachi fuel-delivery system augments the six high-pressure direct injectors in the heads with six lower-pressure port-fuel injectors in the intake plenum. Some aftermarket companies are using this strategy as well to provide the extra fuel required when adding a supercharger or turbos.
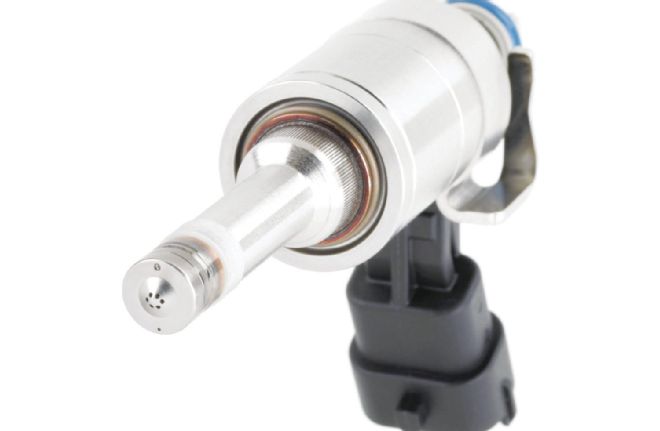 Chevy’s LT1 and LT4 DI systems use piezoelectric fuel injectors that operate in the 60-volt range, which are capable of quickly opening the injector’s hardened, stainless-steel pintle valves at fuel pressures exceeding 2,000 psi. The injectors’ conical spray pattern must be carefully matched to the piston shape and chamber design, so DI injectors are usually application-specific.
Chevy’s LT1 and LT4 DI systems use piezoelectric fuel injectors that operate in the 60-volt range, which are capable of quickly opening the injector’s hardened, stainless-steel pintle valves at fuel pressures exceeding 2,000 psi. The injectors’ conical spray pattern must be carefully matched to the piston shape and chamber design, so DI injectors are usually application-specific.
The good news is that because of the charge cooling, DI engines are nowhere near as detonation-prone as a PFI engines. Copeland confirmed that he has seen boost as high as 18 psi on 93-octane gas without detonation in testing at GM, but the increased compression and greater control over injector timing has also led to less boost being required to create horsepower. “Five or six psi with the right tune will easily put you in the 600hp range,” Behan told us.
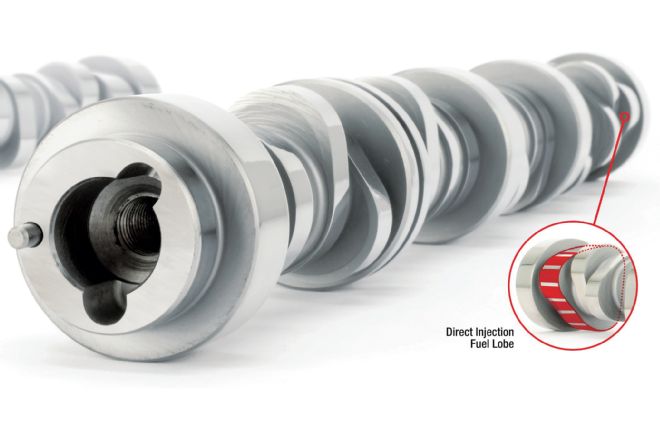 Comp Cams was first to market with camshafts with custom DI pump lobes, and offers four different lobe profiles to drive the DI injection pump.
Comp Cams was first to market with camshafts with custom DI pump lobes, and offers four different lobe profiles to drive the DI injection pump.
The real challenge is the fueling capabilities and how to properly address them. The LT1’s injection pump drives off a special 5.7mm-lift three-pointed lobe on the cam. LPE has been experimenting for the past 15 months on the dyno to properly address and overcome fuel supply and durability issues. While the in-tank electric pump is good to around 800 hp, Copeland tells us the DI injection pump with stock cam configuration is capable of “exceeding 625 hp.” After that, it’s time to address the lobes on the camshaft, which presents its own interesting issues as rpm increases, since the pump is driven by a large-diameter lifter. While four- and five-lobe cams are now available, for its future plans, Copeland states that LPE prefers the dynamics of three lobes. “Currently, we use something in the 7mm lift zone,” he told us.
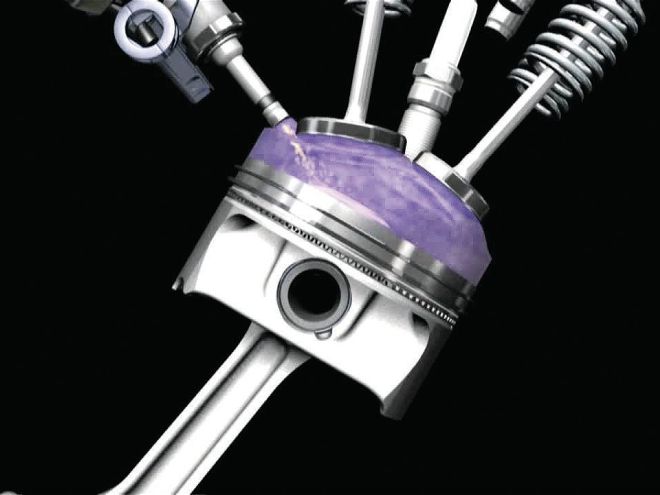
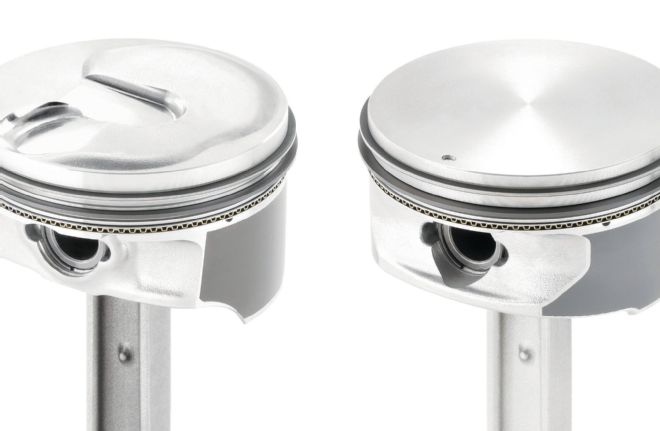 In non-DI engines (right), the piston design is typically featureless or features valve reliefs, but in DI the piston (left) design is critical to efficiency. The injector is aimed at a bowl on the piston surface that is designed to send the fuel toward the spark plug.
In non-DI engines (right), the piston design is typically featureless or features valve reliefs, but in DI the piston (left) design is critical to efficiency. The injector is aimed at a bowl on the piston surface that is designed to send the fuel toward the spark plug.
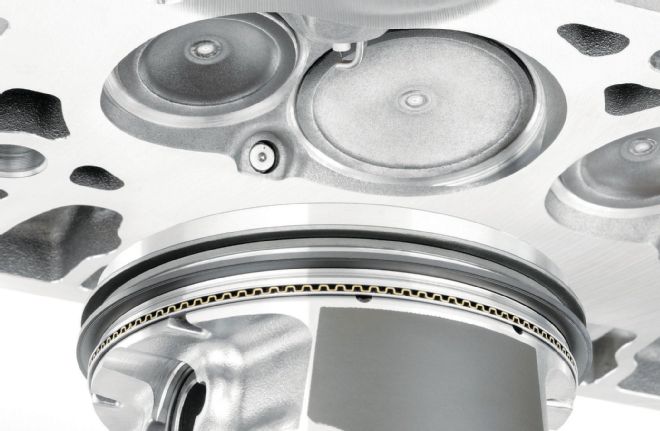 Because DI asks the spark plug to light an extremely pressurized fuel charge very quickly, the ignition system has to be stepped up and spark-plug gaps are usually tightened up as well to prevent blowing out the spark.
Because DI asks the spark plug to light an extremely pressurized fuel charge very quickly, the ignition system has to be stepped up and spark-plug gaps are usually tightened up as well to prevent blowing out the spark.
Similar to how the diesel performance world has addressed its fueling issue with higher-capacity direct-injection pumps (or even dual-injection pumps), LPE is also working on upsized DI pumps that will be available once testing is complete. “We don’t want more pressure, but you can push more volume and stock injectors respond well.” If your needs go beyond that, Behan tells us he sees another crossover from the diesel world eventually arising: modifying the injectors themselves. It’s common for high-output diesel engines to go for higher flow rates, since in Copeland’s words, “Diesel is kind of like a Top Fuel engine—the more fuel you can dump in, the more power it will make.” To be clear, gasoline DI does not work the same, since ignition relies on a spark firing system rather than a diesel’s compression ignition.
 Copeland tells us Lingenfelter engineers have spent hundreds of hours on the dyno testing every practical option for its DI packages and is currently developing the next phase of fueling that will involve custom ground camshafts paired with higher-flow direct-injection pumps.
Copeland tells us Lingenfelter engineers have spent hundreds of hours on the dyno testing every practical option for its DI packages and is currently developing the next phase of fueling that will involve custom ground camshafts paired with higher-flow direct-injection pumps.