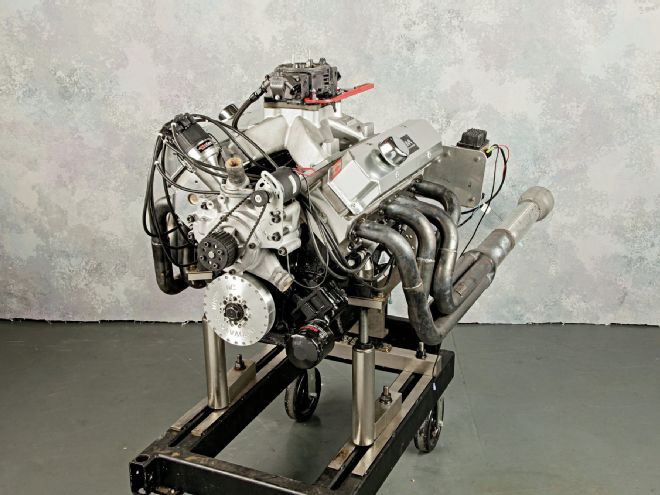
In the Mopar world the Hemi revels in superstar status, while the related big-block wedge is the quiet hero providing power to the masses. Built in large numbers from 1958 through 1978, the wedge came in tall-deck and low-deck configurations, in displacements from 350 to 440 ci. While the Hemi's exotic layout deservedly garners attention, it is the very simplicity and commonness of the big-block wedge that makes these engines attractive. Simple, straightforward, and rugged, the Wedge could be found in all manner of Chrysler products, powering everything from factory muscle cars to trucks, boats, motorhomes, and even industrial units.
Though out of production for decades now, the Wedge Mopar is still readily available and remains relatively cheap to build. These days the most popular combinations are built on either the low-deck 400 (B type) or the tall-deck 440 (RB type), the biggest bore versions of their respective series. Jesse Robinson of Robinson Rutters Auto Machine (RRAM) is a long-time Mopar fan, and recognizes the capabilities of the Chrysler Wedge. Building an engine for the 2013 AMSOIL Engine Masters Challenge, Robinson had the ideal venue to showcase the engine's potential, and RRAM's ability to tap into that potential.
Modified Production
Robinson started with a production 400 block, a configuration with a stock bore and stroke of 4.342 by 3.375 inches, and produced from 1972 to 1978. The short-stroke 400 is readily upsized with a bump in crank stroke, with a wide range of aftermarket 'shafts available. Nevertheless, Robinson turned to the popular approach of using a factory 440 crank in the 400 block, which required the main journal diameter to be reduced to the 400 dimension. This alone would up the stroke to 3.75 inches. Taking things one step further, the rod journals were offset ground to the big-block Chevy 2.200-inch dimension, allowing the swing to be increased to 3.900 inches. While diehard Mopar purists may be appalled by the thought of Chevy parts in a Chrysler Wedge, the 2.200-inch rod journal allows use of big-block Chevy rods, which really opens up the rod and bearing selection, and improves crankcase clearance. This modification is such an advantage that many aftermarket crankshafts are built to this specification.
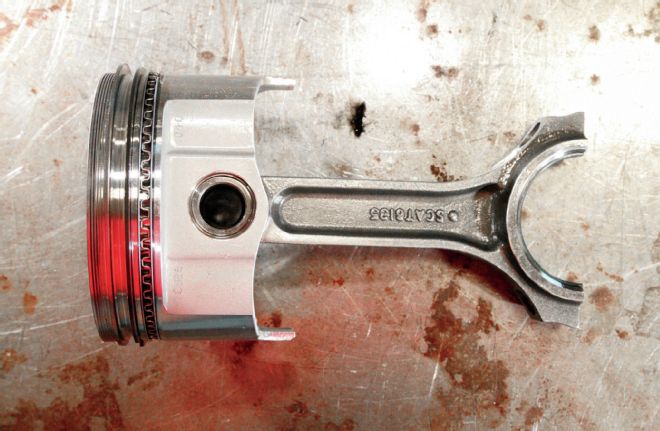
With a clean-up bore to 4.360 inches and the 3.900-inch stroke, the displacement of the engine increased sizably to 466 ci. With the Chevy journals, there are a wide range of rod lengths available. Here Robinson bucked conventional Mopar long-rod wisdom and went with a short-rod arrangement opting for a set of Scat I-beam rods in a 6.135-inch length. Robinson relates: "I have been rethinking the rod length presumptions, and looked to gain the higher piston speeds near TDC with the short rod setup. In an engine like this I see no disadvantages to the short rod, but I did need to cut extra material from the counterweights for piston clearance."
This stroke and rod length combination worked out to allow an off-the-shelf 440 piston from Icon to be used. Robinson explains: "The Chevy rod is so popular these days that many manufacturers are building parts with this in mind. These Icon pistons feature a Chevy spec 0.990-inch pin, so they are compatible at the rod's small end." Although the forged Icon pistons were an off-the-shelf item, to meet the compression ratio limit of 11:1 for the Engine Masters competition, the pistons were heavily modified. Robinson says, "The pistons actually started out as flat tops, but with the small chambers in the heads, we needed to machine them to a dish, and add the large valve relief for volume. I preserved as much of the squish area around the circumference as practical, and brought the volume to where it needed to be to meet the required specification."
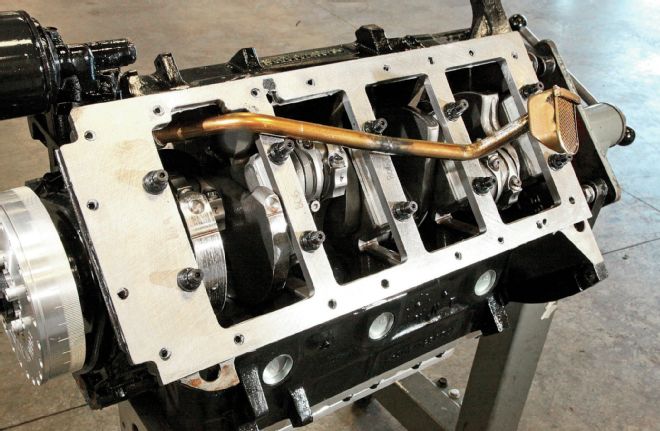
A factory block and crank is not what you would normally expect to serve as a foundation for an engine producing north of 750 hp. This factory Mopar 400 Wedge gains considerable beef via RRAM’s custom fabricated girdle arrangement. A factory forged crank from a Mopar 440 provides 3.900 inch of stroke thanks to an offset grind to big-block Chevy journals.
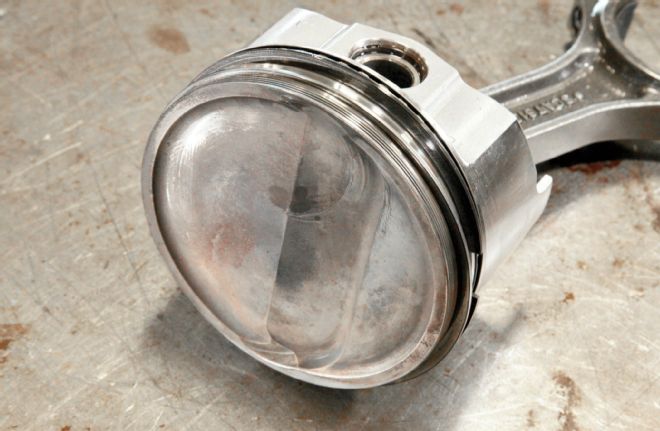

Pistons are Icon units for a 440 Mopar application with a Chevy 0.990-inch pin. These are readily available in-stock units, but the crown was heavily modified to reduce the compression ratio to this dished configuration.

To top the engine, RRAM started with Procomp cylinder head castings, which are manufactured with material to accommodate a Max Wedge sized port, and can accommodate even larger custom port forms.
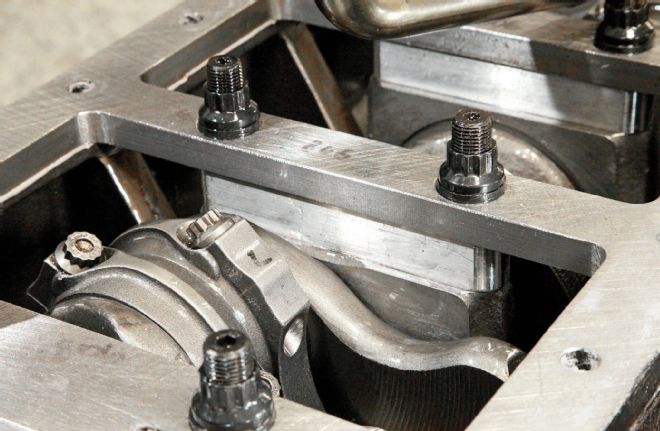

This detail reveals the magic stack that ties the bottom end together, starting with the stock main caps machined to be topped with a billet aluminum spacer, which in turn mates to a custom 1/2-inch steel girdle, all cinched together by premium ARP fasteners. The deep skirted Mopar block is ideally suited to this kind of reinforcement.

The Icon pistons are made for a common 1/16-1/16-3/16 ring pack, which is handled by a conventional ring set from MAHLE Clevite. Rods are Scat I-beam units measuring 6.135-inch, center to center.
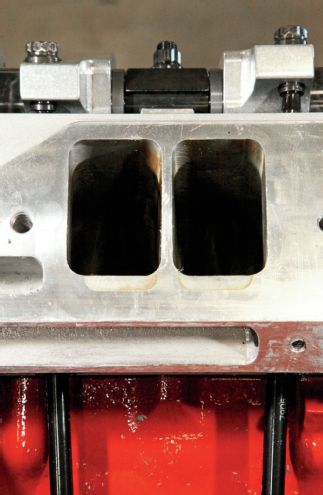
To feed the Wedge, RRAM radically altered the port size and position, going to a wide raised-runner layout. Note the original port size indicated by the epoxy filled area on the floor. The available space between the pushrods is the limitation to port width. The offset intake rockers allow for significant enlargement.
One of the areas where the factory Hemi has a distinct advantage over the Wedge is in the bottom end. Unlike the cross-bolted Hemi, the deep-skirted Wedge blocks all carry two-bolt mains. Here a girdle can add significantly to the structure, tying the main caps to the heavily webbed crankcase. Although manufactured girdles are available, Robinson was not satisfied with their design and machined his own. "I started with a half-inch-thick ground steel bedplate, and machined the girdle. The engine uses factory main caps, which were machined to accept aluminum spacers between the cap and girdle. The cap and spacer assembly was sized at .001-inch proud of the pan rail, allowing the girdle to solidly tie the bottom end together." The ARP studs pass through the cap, spacer, and girdle, securing the assembly.
Power Parts
Although many of the components in the bottom end, including the block itself, were based on OEM components, the modifications resulted in tremendously improved power handling capabilities. To generate that power, the heads, cam, and induction are the key. Robinson put a great deal of emphasis on the cylinder head development program, starting with a set of Procomp castings. Robinson says, "I started by angle milling more than I had ever done before, which really improved the chamber. The other major change was to move the cylinder head over on the dowels toward the centerline of the block. This improves the valve position in the cylinder, and I took it out as far as practical with the available material. It was a time-consuming process, taking four hours of machine time per head just to elongate and spot face the boltholes. From there, it was an extensive rework of the ports, moving the intake ports up and taking them out the widest dimension possible."
The heads use Ferrea valves in 2.250/1.750-inch sizes, with hollow stems to reduce weight and improve stability at high rpm, an important consideration with an aggressive hydraulic roller cam. The custom Competition Cams grind measures 256 degrees of duration, and delivers .752-inch lift, moving the valves in a hurry through a T&D shaft-mounted rocker system. Getting the hydraulic roller to cross the 7,000-rpm mark proved difficult, as Robinson details, "I was having trouble with valvetrain stability at 6,700 rpm, and power just dropped off a cliff at that point. I was using a conventional hydraulic roller lifter, and then changed to a limited-travel design from Scorpion. That completely solved the problem, letting the engine pull cleanly to well over 7,000 rpm."
Feeding the cylinder heads is an Indy single-plane intake manifold, a design that has earned an outstanding reputation among Mopar wedge builders. The work to the manifold primarily involved matching the modified port size and location of the cylinder heads. Considerable material was removed to match the port width, while the floor of the runners was filled to meet the height of the raised intake runners. The plenum area required little attention. Carburetion is handled by a 950-cfm Holley Ultra HP, a unit that Robinson found impressive: "There were not any special tricks in the carb, just jetting changes. The fuel curve looked very good with a minimal amount of time needed to get there."
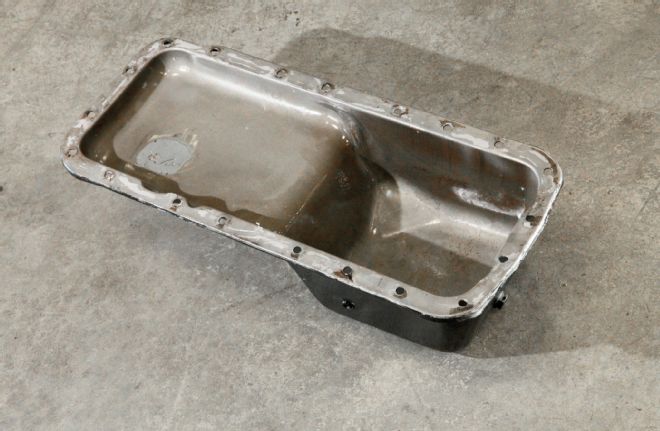

Holding the oil is a production truck oil pan, with no additional windage tray, baffles, or scraper. The only modifications here were dimpling to clear the rear main studs.
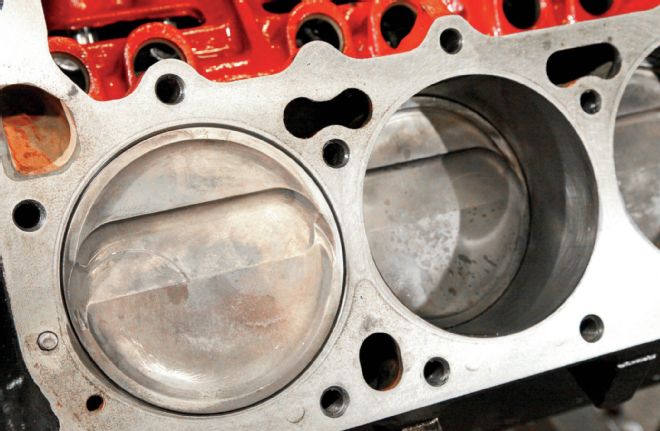

The Mopar 400 was factory endowed with the largest bore of any Chrysler big-block, at 4.342 inches. RRAM simply opened the bores to the first standard oversize, at 4.360 inches. Although their bore sizes are similar, Jesse Robinson of RRAM tells us the low-deck 400 block is considered to be more rigid than the taller 440 block.
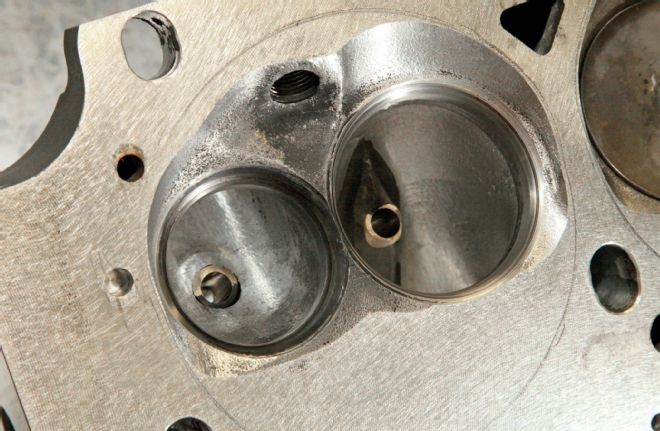

Heavy angle milling dramatically improves the combustion chamber form, and reduces airflow-robbing cylinder wall shrouding. The heads were also relocated on their dowels, moving the valves to a more advantageous position relative to the cylinder wall. Note the extensive elongation of the nearby head bolthole to accommodate the modification.

Valves are hollow-stem units from Ferrea, selected to reduce weight for improved valvetrain stability. The intake valves measure 2.250 inches, while the exhaust spec at 1.750-inch diameter.

A COMP billet hydraulic roller camshaft operates Scorpion limited-travel lifters. Robinson found the limited-travel lifters added considerably to the rpm capacity of the engine. The cam measures 256 duration, with .752/.705-inch lift via 1.6/1.5 ratio rocker.

Delivering the airflow to the heads is an Indy single-plane manifold, modified with extensive porting and filling to match the work done to the cylinder heads.
Another item that Robinson found to be outstanding was the FireCore distributor. "As soon as you pick this distributor up, you will be impressed by the manufacturing quality. It's just a beautifully made part that functions perfectly." The engine was also equipped with a FireCore spark plug wire set, while ignition is handled by an MSD 7AL. Up front, Robinson fitted an Innovators West crankshaft damper, and a replacement-style PRW water pump spun by a remote electric drive. The exhaust headers proved to hold an important influence on the power curve, as Robinson relates, "The headers are a Schoenfeld Sprint Car–style dyno header, with stepped 1 7/8 to 2-inch primary tubes and 3 1/2-inch collectors. We found tuning the collector length had a big effect on the torque at the bottom end of the rpm range. There was a pronounced dip in torque at the bottom of the curve, and by altering the collector length we were able to tune it completely out."
Dyno Duty
In qualifying eliminations at the 2013 Engine Masters Challenge, the power of the wedge was on display for all to see. We'd have to say that Robinson and the crew at RRAM took advantage of the strengths inherent in the Mopar big-block, while making all the right moves to address its shortcomings. While a stock-block might become questionable at the 600hp level, Robinson's modification to the bottom end has seen this engine operate reliably over countless dyno pulls at significantly higher output. How high? We had 755 hp on display recorded at 6,300 rpm, with 674 lb-ft of torque twisting the dials at 4,800 rpm. The key factor to extracting that kind of power from a Wedge was giving it what it lacked from the factory: airflow. The expertly applied modifications to the cylinder heads, along with the effective induction, camshaft, and valvetrain unleashed massive power from the Wedge. The crafty modifications to the block, along with the right aftermarket parts ensure that it will live. RRAM stepped up this simple looking wedge to a power level that would make a Hemi proud!
By The Numbers 466 Mopar Big-Block
Bore: 4.360 inches Stroke: 3.900 inches Displacement 466 ci Compression ratio: 11.48:1 Camshaft: custom COMP hydraulic roller Valve lift: .752/.705-inch Rocker and ratio: T&D 1.6/1.5:1 Piston rings: MAHLE Clevite 1/16-1/16-3/16-inch Piston: Icon forged Block: Production Mopar 400 Crankshaft: Production Mopar 440 Rods: Scat 6.135-inch Cylinder head: Procomp Electronics Intake valve diameter: 2.250 inches Exhaust valve diameter: 1.75 inches Intake manifold: Indy Carb: Holley 950 Ultra HP Header: Schoenfeld stepped primary, 1?- 2-inch Ignition: Firecore/MSD Damper: Innovators West Oil Pan stock Mopar Fuel VP 100 unleaded Oil AMSOIL 15w50On The Dyno 466ci Mopar
RPM: TQ: HP: 3,000 495 283 3,100 511 301 3,200 533 325 3,300 553 347 3,400 570 369 3,500 585 390 3,600 595 408 3,700 604 426 3,800 607 439 3,900 606 450 4,000 607 462 4,100 614 479 4,200 625 500 4,300 635 520 4,400 640 537 4,500 647 554 4,600 660 578 4,700 670 600 4,800 674 616 4,900 672 627 5,000 668 636 5,100 666 647 5,200 666 659 5,300 667 673 5,400 667 686 5,500 667 699 5,600 666 710 5,700 664 721 5,800 662 731 5,900 656 737 6,000 651 744 6,100 645 749 6,200 639 754 6,300 629 755 6,400 618 753 6,500 605 748 6,600 590 742 6,700 575 733 6,800 565 731 6,900 551 725 7,000 542 722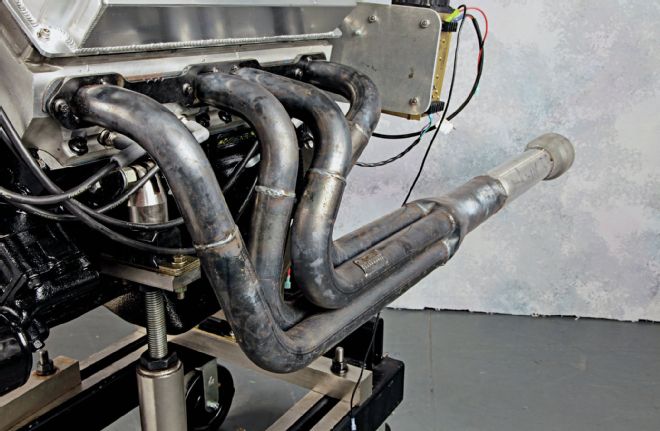
The headers are a Sprint Car–style stepped primary set from Schoenfeld. The long collector was a result of testing by RRAM, finding an improvement in low-end torque.

One item that Robinson specifically pointed out was the distributor from Firecore. As he put it, "I don't know how they can manufacture a unit this nice at the price they do." Firecore wires, and an MSD ignition box complete the system.
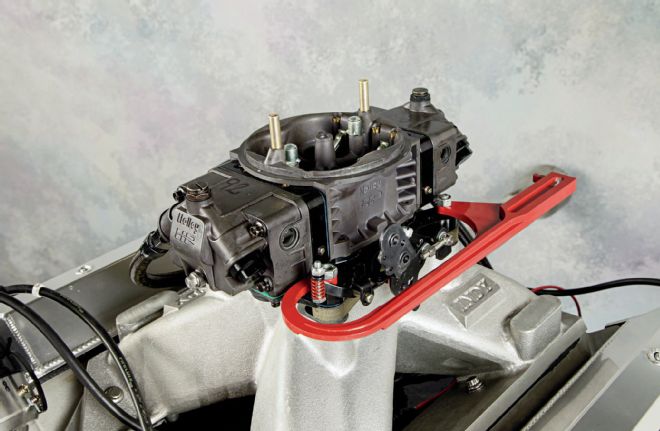

A Holley 4150 carb supplies the air/fuel mixture, in this case a 950-cfm Ultra HP. Robinson tells us that other than minor tuning-related changes, the carb is out-of-the-box stock, and was remarkably easy to set up.
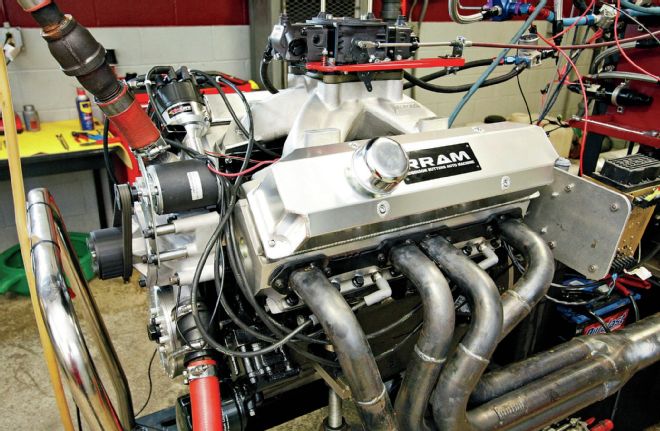

On the dyno at the 2013 AMSOIL Engine Masters Challenge, RRAM's deceptively simple looking Wedge delivered remarkable power, recording 755 hp and 674 lb-ft of torque.

The RRAM crew at the 2013 AMSOIL Engine Masters Challenge (left to right): Jesse Robinson, Joe Rutters, Ron Maclean, and Bryant MacDonald.