
Burbank, California’s Lucian Bartoletti is a proud member of the legendary Road Kings of Burbank car club. Founded in 1952, the club’s been in existence 61 years. Its storied membership rolls have included the likes of Tommy Ivo, Don Prudhomme, and Bob Muravez, among others.
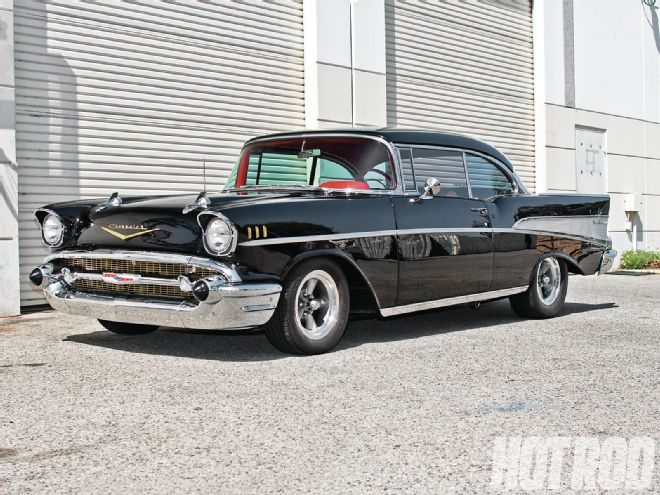 Built for cruising, the 1957 has a year-old 377 small-block, a T5 overdrive, 3.73:1 gears, 11-inch front disc brakes, and custom interior mods.
Built for cruising, the 1957 has a year-old 377 small-block, a T5 overdrive, 3.73:1 gears, 11-inch front disc brakes, and custom interior mods.
Bartoletti built his 1957 Chevy for long-distance cruising with his buddies. A year ago, he dropped in a built, 377ci small-block Chevy with a healthy Comp Cams bumpstick backed up by a World Class T5 five-speed overdrive trans and an original ’57 Chevy drop-out third-member rearend equipped with 3.73:1 gears and Positraction.
 Car owner Lucian Bartoletti has owned his 1957 Chevy for 11 years, nearly as long as he’s been in the Road Kings car club.
Car owner Lucian Bartoletti has owned his 1957 Chevy for 11 years, nearly as long as he’s been in the Road Kings car club.
From day one, the engine had irritating driveability issues. “After I put the motor in the car in 2012,” Bartoletti relates, “We drove it to Morro Bay to attend the annual car show. The car ran bad. It was dripping fuel internally from the carb. I almost washed the motor down on the way.” Bartoletti found and fixed the leak, but even so, the car didn’t drive right. Under normal (not dead-cold) start-up conditions, there was an intermittent cough back through the carb, as well as an off-idle stumble when pulling away from a stoplight at light throttle: “I couldn’t engage the clutch without the carb coughing back.” The engine also ran rough, missed, and surged in high gear (Overdrive) between 1,800 and 2,000 rpm, “the exact rpm for freeway cruising in high gear.” Yet it ran fine under wide-open-throttle acceleration.
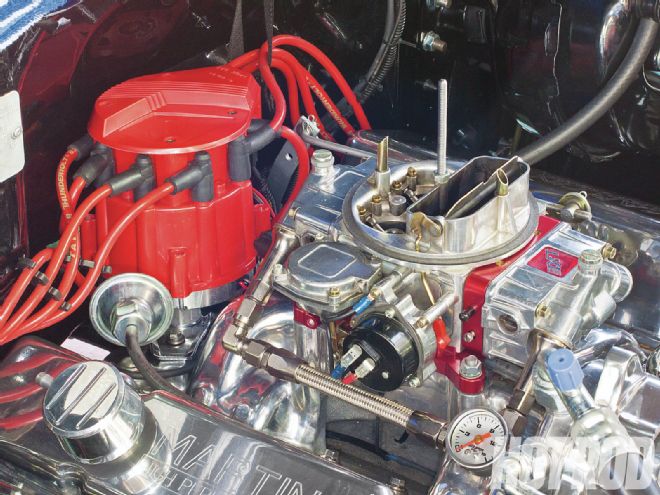 The new motor experienced intermittent missing, surging, and coughing through the carb. Was it the carb, the ignition, or both?
The new motor experienced intermittent missing, surging, and coughing through the carb. Was it the carb, the ignition, or both?
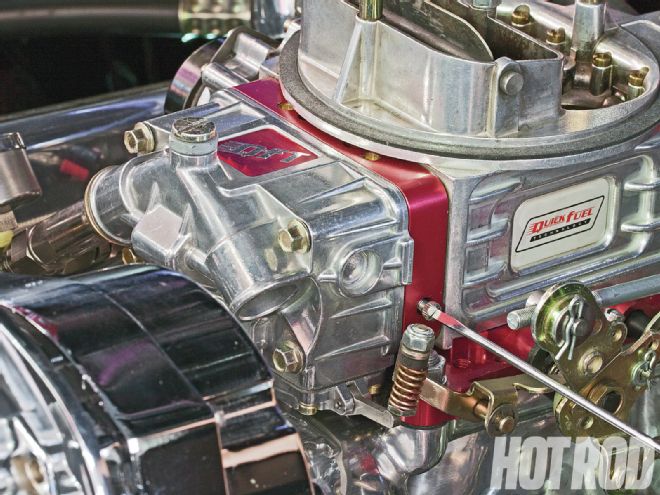
So-called “experts” told Bartoletti the problem “had to be in the carb,” so over the next year, he intermittently played with its calibration. To reduce off-idle stumble, Bartoletti increased the accelerator-pump shooter size, changed the pump cam, and adjusted the pump actuator linkage to preload the pump-diaphragm lever so it moved as soon as the throttle linkage moved. Trying to resolve his unstable part-throttle, steady-state-cruise issue, he installed a quicker-opening power valve and slightly leaned out the main jets. These changes helped a little, but the problem still persisted—so he asked us for help.
We sent the 1957 to Granatelli Motorsports. Based on the questions I asked him during his initial interview, in the days leading up to his HOT ROD to the Rescue appointment it occurred to Bartoletti that he’d never considered the possible ignition side of the equation. So before driving the car out to Granatelli’s place, Bartoletti says he “bumped the timing a few degrees, from an initial timing of 10 degrees BTDC to 12 degrees BTDC. On the way over, it seemed to have improved a little.”
So close, so close! As it turns out, by the time the car arrived at Granatelli, Bartoletti was about 75 percent of the way to resolving his problems…he just didn’t realize it.
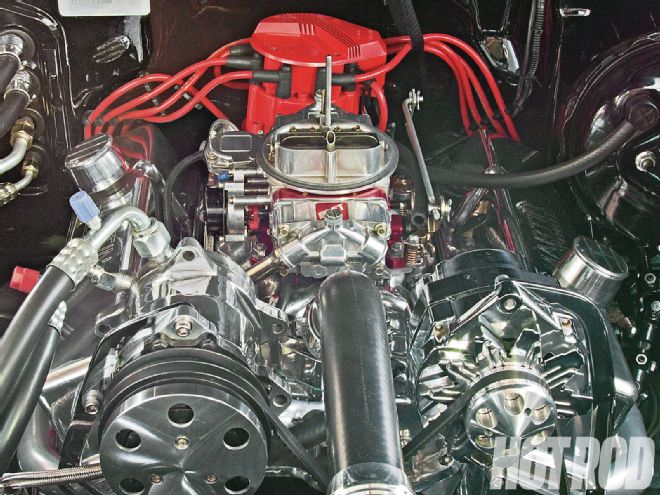 The 9.6:1, 377ci small-block has aluminum heads, a Quick Fuel 750-cfm vacuum-secondary Slayer carb atop a dual-plane air-gap intake, a generic GM HEI distributor clone, and headers. Its fairly big Comp Cams XR282HR Xtreme Energy hydraulic-roller cam specs out at 230/236 degrees at 0.050 and 0.510/0.520-inch valve-lift with a 110-degree lobe-separation angle.
The 9.6:1, 377ci small-block has aluminum heads, a Quick Fuel 750-cfm vacuum-secondary Slayer carb atop a dual-plane air-gap intake, a generic GM HEI distributor clone, and headers. Its fairly big Comp Cams XR282HR Xtreme Energy hydraulic-roller cam specs out at 230/236 degrees at 0.050 and 0.510/0.520-inch valve-lift with a 110-degree lobe-separation angle.
Located about an hour west of Los Angeles in Oxnard, California, Granatelli Motorsports is renowned as a manufacturer and distributor of late-model tuner products for today’s high-tech EFI cars, but it also does in-house tuning on all makes of early and late hot rods. Frank Distaso, Granatelli’s resident old-school carb and ignition guru, has been associated with the Granatelli clan since their 1960s Indy racing program. For years, he also ran Distaso Automotive in downtown LA, one of the big dynotune outfits back in the muscle-car era. Distaso can practically tell what’s wrong with an old car by breathing on it—but it sure helps to have owner J.R. Granatelli’s state-of-the-art Mustang chassis dyno to fall back on.
 Tuner Frank Distaso (left), J.R. Granatelli, and assistant (aka “daughter”) Audrianna Granatelli are on the job.
Tuner Frank Distaso (left), J.R. Granatelli, and assistant (aka “daughter”) Audrianna Granatelli are on the job.
You might think that a vacuum leak could be the cause of Bartoletti’s stumble and tip-in “cough-back” through the carb, but Distaso’s instincts born of decades of experience pointed in another direction. “When I saw the cam specs—230/236 degrees at 0.050—I knew instinctively there were no vacuum leaks; it was just a fairly big cam. Not that the average guy shouldn’t check for vacuum leaks first. But I had a strong feeling the ignition timing was too retarded for the cam. Listening to the car, I also felt the carb was not quite right. I also took a look at the spark plugs. The porcelain and top outer wall were black, indicating the car was running rich. There was also a puff of black smoke out the exhaust when you stepped into it.” Both carb and ignition problems can cause an over-rich condition, so he took a look at both.
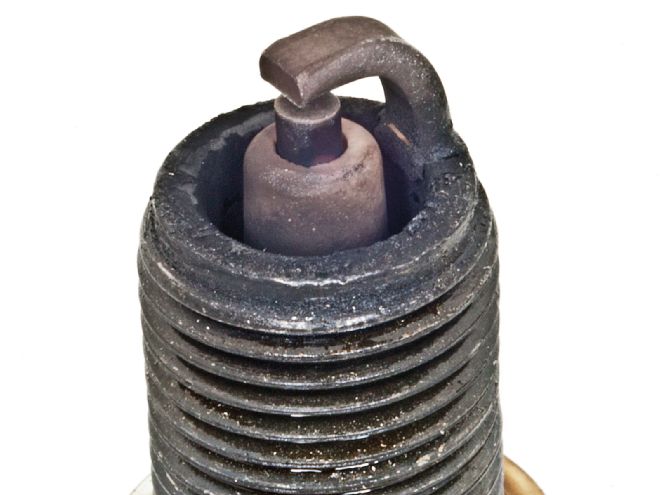

 Spark-plug coloration can tell you a lot about what’s going on inside an engine. Like many old-school tuners, Distaso uses a reading light to examine the spark plugs. Unlike this brand-new plug, on the ’57 the porcelain surrounding the center electrode was a dark gray-black, indicating a rich mixture. This could be caused by a misadjusted carburetor, retarded timing, or both.
Spark-plug coloration can tell you a lot about what’s going on inside an engine. Like many old-school tuners, Distaso uses a reading light to examine the spark plugs. Unlike this brand-new plug, on the ’57 the porcelain surrounding the center electrode was a dark gray-black, indicating a rich mixture. This could be caused by a misadjusted carburetor, retarded timing, or both.
Distaso started by checking and adjusting the float level. On the primary side it was slightly high, contributing to the rich idle. The idle-mixture screws were adjusted too rich as well. No tach or vacuum gauge for this ace old-school tuner: Distaso does idle mixture adjustments entirely by ear, fiddling back and forth with the screws to get the best, cleanest idle. “Look at the engine. Listen to the engine. It’ll tell you what it likes. I go for the smoothest idle I can get out of it. Turn the screws in until the idle gets rough, then come out very easy on one side until it sounds fairly decent, then do the same on the other side. Go back and forth two or three times until you get the best quality.”
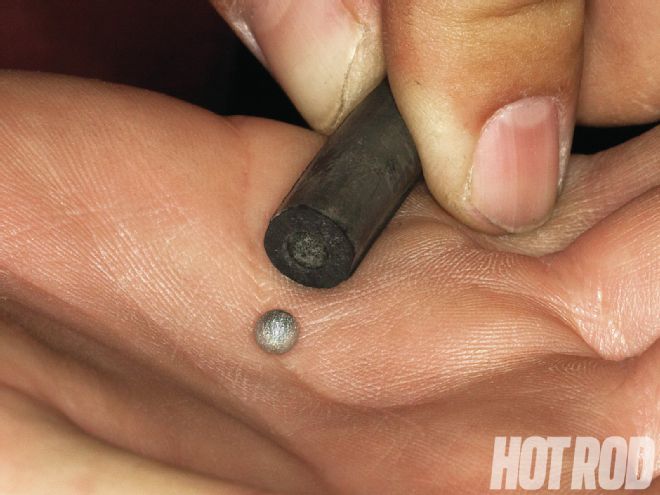 An easy fix: Adjust the carb’s float level and idle mixture, add more initial timing, and plug the vacuum-advance line with a ball bearing.
An easy fix: Adjust the carb’s float level and idle mixture, add more initial timing, and plug the vacuum-advance line with a ball bearing.
Other than basic carb adjustments, the internal calibration proved to be correct for the combo. Distaso particularly praised Bartoletti’s accelerator pump lever preload setting: “As soon as I cracked the throttle, I got a nice spurt out of the shooter.”
 “The idle mixture screws were so far off!” Distaso exclaimed. The ace adjusts idle mixture screws by sound until he achieves the smoothest idle. When Distaso rebuilds a carburetor, “the initial setting is two turns out from bottoming. That’s only a start point—then it’s all by ear. Be sure the float levels are right before you adjust the idle mixture.”
“The idle mixture screws were so far off!” Distaso exclaimed. The ace adjusts idle mixture screws by sound until he achieves the smoothest idle. When Distaso rebuilds a carburetor, “the initial setting is two turns out from bottoming. That’s only a start point—then it’s all by ear. Be sure the float levels are right before you adjust the idle mixture.”
“I was chasing my tail. I never associated my initial timing with the cough through the carburetor.”
— Lucian Bartoletti
Overall, the distributor’s centrifugal advance curve was pretty smooth. It started at 1,100 rpm and was all in by 3,200, developing 11 degrees at the distributor (22 degrees as read at the crank). “I liked the centrifugal curve as it was,” Distaso explains. “It’s quick enough. HEI centrifugal curves, in my experience, were always pretty close to what I wanted.”
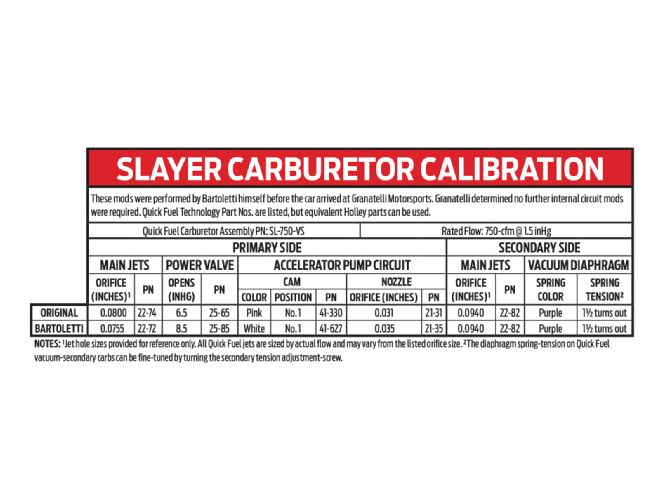
With 12 degrees initial advance, the engine had a total of 34 degrees at the crank. According to Bartoletti, that’s close to what the original engine builder recommended. But Distaso maintains that’s not enough for the motor’s healthy cam. “As a general rule, start at 36 degrees total as a baseline. If the car cranks hard or kicks back through the starter, back off on the initial timing, and put more in the distributor.” With the car on the chassis dyno, trial-and-error runs determined that this engine liked 16 degrees initial, for a total of 38 degrees with the centrifugal advance all-in. With these specs, the car still cranked OK and started up with no kick-back, and it also responded better off idle.
The HEI’s vacuum advance was another story. Even after all adjustments were finalized, Bartoletti had only 10 inches of manifold vacuum at idle. Strangely, this didn’t seem to adversely affect his large power-brake booster, but it did play havoc with the distributor’s vacuum-advance mechanism. When connected to ported vacuum, there was already 5 inches of vacuum advance at idle—it should have been virtually zero. Conversely, going to manifold vacuum would have added too much timing at idle.
And the ported vacuum kept climbing to as high as 24 inches; there was even some ported vacuum at full-throttle, when it should have declined back to near zero. Additionally, at the car’s typical 2,000-rpm cruising speed, Distaso says the car kept “hunting in and out of vacuum advance. Manifold vacuum or ported vacuum—on this car, it just didn’t make any difference.”
Apparently, the large cam’s low vacuum output plus the mild 2.33:1 effective final-drive ratio with the T5’s 0.63:1 overdrive gearing put the vacuum advance right in the sour spot. Distaso’s simple solution: Just block it off.
Running both at part-throttle and full-throttle on Granatelli’s Mustang dyno under various loads, plus on-road testing, confirmed that Bartoletti’s original issues were successfully resolved. At part-throttle tip-in, the 1957 no longer kicks back through the carb. But with the gross off-idle cough-back resolved, Bartoletti is now noticing a very slight lurch pulling gently away from a traffic signal. Tuning this out would require better matching the flywheel, clutch disc, and pressure-plate combo to the big-cam, 3,900-pound, “heavy Chevy.”
At cruise, the occasional miss and lean surge have vanished. However, if the throttle is slammed wide open at around 1,900–2,000 rpm in overdrive—as could occur when accelerating quickly to pass a slow-poke—the engine remains a little lazy; there’s no bog, it just takes a while for it to really start winding up. The obvious crutch is downshifting to a lower gear, like an automatic does when it kicks down. Ultimately, Bartoletti could achieve quicker High-gear response by installing steeper gears so at his 65-mph cruise-speed the motor operates within the cam’s 2,200–5,800-rpm powerband (sidebar). But steep gears and their associated four-series Posi carriers for the old Chevy drop-out rear are getting hard to find.
A week after the fix, Bartoletti drove to the 2013 Morro Bay show with no problems. That’s about a 250-mile round-trip. Under full throttle, the car pulled strong in all gears. Going north through the mountains out of Los Angeles, Bartoletti says “it went right up that long, steep climb on the I5 Grapevine in Fifth-gear-overdrive with no problems. It never did that before. It used to surge and now it doesn’t. I even had the air on without a problem!” The car doesn’t seem to miss the vacuum advance; Bartoletti reports that gas mileage is actually slightly improved.
 Repeated dyno runs at both part- and full-throttle were made on Granatelli’s state-of-the-art Mustang AWD1200 chassis dyno. The dyno helped resolve the gearing/timing issues at Bartoletti’s 2,000 rpm cruise-speed, while also proving the carb’s WOT calibration was correct.
Repeated dyno runs at both part- and full-throttle were made on Granatelli’s state-of-the-art Mustang AWD1200 chassis dyno. The dyno helped resolve the gearing/timing issues at Bartoletti’s 2,000 rpm cruise-speed, while also proving the carb’s WOT calibration was correct.
A drivetrain must be a matched combo. Trans and rearend gearing must match the engine’s characteristics as well as the vehicle weight. What appears to be a carburetion problem can also be related to the ignition. “People need to learn that a big camshaft needs big timing,” Granatelli points out. “Lucian had a lumpy cam; he retarded the timing, when he should have advanced it.” Adds Distaso, “I know Lou likes a rumpity-rump cam, but he has such a nice cruiser. If it were me, I would put in a milder cam, a smaller carb, and a little steeper gear ratio. He’d have a near-perfect car.” And at just 9.6:1 static compression, Bartoletti could gain more power and further enhance driveability by upping the squeeze to 10.0:1.
The Gear-Ratio Solution
With Bartoletti’s present healthy Comp hydraulic roller cam, in overdrive at his typical 65-mph cruising speed, engine rpm is below the cam’s 2,200–5,800-rpm operating range, meaning the car is inherently slow-revving and lazy if he quickly accelerates in High-gear. The ultimate fix would be moving up to steeper rearend gears.
To figure out what changes are needed, use the basic “speed-in-gear” equation:,
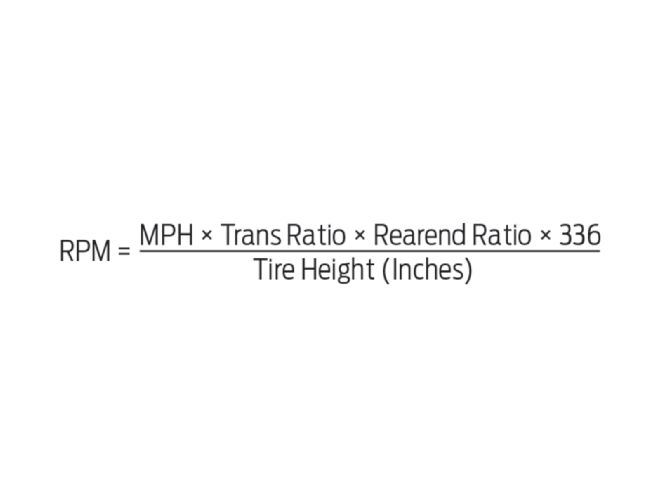
Bartoletti’s T5 has an 0.63:1 overdrive ratio. The rearend sports 3.73:1 gears. His P245/60R15 BFGoodrich Radial T/A tires are 26.6 inches tall. At 65 mph, engine speed is just 1,929 rpm:

What would it take to get the cruise rpm up to at least 2,200, the bottom of the cam’s operating range? Like any formula, the equation can be “flipped” to solve for any one missing element, in this case, the rearend gear-ratio:

The equation tells us Bartoletti needs at least 4.25:1 gears. But that ratio isn’t offered, so he’d have to move up to the next numerically steeper ratio. For the early Chevy drop-out rearend, that would be 4.56:1. Plugging the new gears into the equation and solving for rpm, we see that at 65 mph, engine speed comes in at 2,359 rpm.

Richmond offers 4.56:1 gears for the early Chevy rearend (PN 69-0022-1), but as this is written in June ’13 they are on indefinite nationwide back-order. (Jegs is accepting orders at $334.99.) Bartoletti would also need either a ring-gear spacer for his existing three-series Posi case (Mr. Gasket PN 900A, $41.99 at Jegs) or (preferred for its greater strength and stability) locate a rebuildable actual early Chevy four-series Posi case.
Need Junk Fixed?
If your car has a gremlin that just won’t quit, you could be chosen for Hot Rod to the Rescue. Email us at [email protected] and put “Rescue” in the subject line. Include a description of your problem, your location, and a daytime phone number.