More than any other Detroit marque, this is a name that conjures up a powerful image of luxury and power; the kind that has been flaunted by Cadillac dealers and owners from the beginning of the company's history right up to today. For millions of Americans, Cadillac ownership was the ultimate symbol of "making it," and those who didn't have it, dreamt of it. Detroit owes a great deal to the founders of this company. In fact, the marque's name comes from Le Seur Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac, who established that city as a fur trading post in 1701, and whose name and family crest became the symbol for the car company. Although stylized in modern times to disguise its heraldic provenance, the logo is still in use today.
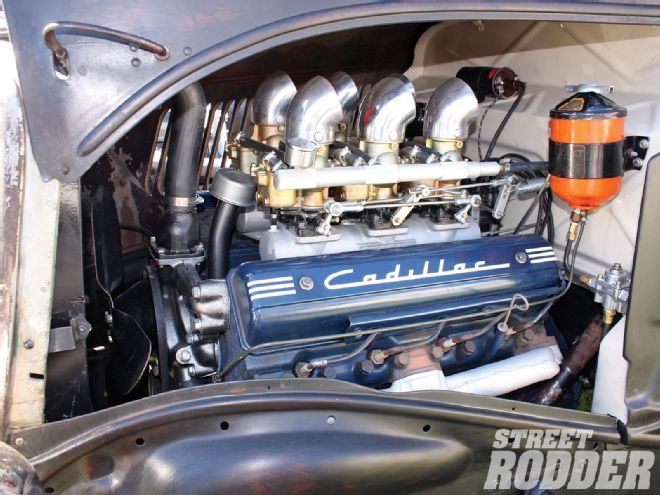
 Our vote for the wildest Caddy ever built is this 441-incher built by John Shields in 1959 for a race boat customer who never picked it up. Restored by the late-Don Tognotti, it has been on display in his Sacramento speed shop for decades. Here's a Hilborn-sucking Potvin blower mounted to the flywheel end of the engine with a Cragar bellhousing and Pribble (Cad specialists back in the day) mounting plate. The other end of the engine has a polished aluminum timing cover and a chromed billet-steel damper that was machined to drive the propshaft.
Our vote for the wildest Caddy ever built is this 441-incher built by John Shields in 1959 for a race boat customer who never picked it up. Restored by the late-Don Tognotti, it has been on display in his Sacramento speed shop for decades. Here's a Hilborn-sucking Potvin blower mounted to the flywheel end of the engine with a Cragar bellhousing and Pribble (Cad specialists back in the day) mounting plate. The other end of the engine has a polished aluminum timing cover and a chromed billet-steel damper that was machined to drive the propshaft.
What is also little known today is that the roots of the company evolved from a group of investors who first backed the inventor Henry Ford at the turn of the 20th century in what was called the Henry Ford Company. Interested in maximum profits, they produced some very expensive cars for the period, and ol' Henry left that avenue behind, forming his own Ford Motor Company to fulfill his dream of an inexpensive car for the masses. In 1902, the original financiers stayed with the high end of the market and became Cadillac, and later a major component of William Durant's General Motors Corporation, forever the major competitor of Ford. Cadillac established its reputation early through the suppliers of their precision tooling and won awards for their use of interchangeable parts, precisely built with no hand-fitting of engine parts or gears, as was common in those days. Cadillac once sent six of their cars to an English motor magazine who had mechanics disassemble them, mix the parts up, and reassemble six cars. The finale was not only starting the cars but driving them for 500 miles with no mechanical failures.
The period of time with which we are concerned in this series of vintage engine profiles is the first OHV era from 1949-62, the major development period for Cadillac powerplants and thus, the favored engines for use in traditional hot rods. Cad and Olds (STREET RODDER, January 2009) both had their new Kettering-design overheads on the market in 1949, with a 303 in the Oldsmobiles and 331-inchers in the heavier Cads. That motor continued until 1956 when Cadillac enlarged the bore to 4.00 inches for 365 cubes. All the Cadillac V-8s we're interested in had tremendous amounts of low-end torque to effortlessly power those heavy road cars. The 365 offered 335 hp in Eldorado trim with three two-barrels. In 1959, the engine was further poked and stroked to achieve 390 ci, which was about the limit for this block's architecture.
 Geoff Miles of The Rodder's Journal has been putting together a choice '29 on Deuce 'rails nicely filled with a '56 365-incher with two Strombergs, Offy intake, Offy valve covers, Vertex mag, and traditional headers made from '36 Ford torque-tubes. (Photo courtesy The Rodder's Journal.)
Geoff Miles of The Rodder's Journal has been putting together a choice '29 on Deuce 'rails nicely filled with a '56 365-incher with two Strombergs, Offy intake, Offy valve covers, Vertex mag, and traditional headers made from '36 Ford torque-tubes. (Photo courtesy The Rodder's Journal.)
The search for more power through bigger displacement led the engineers to come up with a new 390 for 1963. Although it shared the displacement of its predecessor, it shared almost nothing else. The new 390 was designed with future upsizing in mind, yet the engine was 50 pounds lighter and 4 inches narrower than the old 390. Torque was up to 430 lb-ft. After that, this block's next iteration (1964-67) featured 429 ci, 340 hp, and a stump-pullin' 480 lb-ft of torque. Later, Cadillac went to even bigger engines, which make great motors for trucks and for anyone who wants to make a few extra bucks moving houses or pulling stumps. For our examination, the '62 390 is the last of the "vintage" Cadillac powerplants.
Cadillac engines in hot rodding
Everyone on the racing/street performance front in the early '50s recognized the big Cad motors for their potential, yet the price kept these engines out of the hands of tinkerers until enough of the big cars found their way into wrecking yards. When these engines showed up, hot rodders were right there. They were still more expensive than an Olds or Buick and more costly than a Flathead by a big margin, but the Cad motors represented a major power source without requiring much hop-up equipment beyond dual exhausts. The adapter companies jumped right in and the Cads became one of the most swapped brands. The Ford shoeboxes were a very popular receptacle and complete kits for Cad to early '50s Fords were available from Detroit Racing Equipment, who also offered dual-quad manifolds.
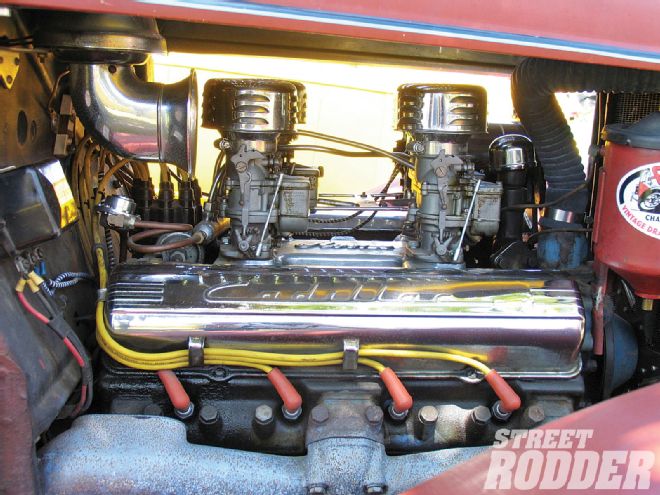 Cadillac engines with their low-end torque could be installed in a street rod without much urgency for hop-up equipment. Even the most risky stroked-and-poked Flathead of 300 ci was little match.
Cadillac engines with their low-end torque could be installed in a street rod without much urgency for hop-up equipment. Even the most risky stroked-and-poked Flathead of 300 ci was little match.
Cadillac engines soon found their way into numerous racing boats and more than a few sports car specials. In fact, most of the popular British Allard K-3 roadsters sold without engines and designed for '50s road racing were fitted by their American importers with Cadillac engines.
Wealthy racing enthusiast Briggs Cunningham made two entries at the '50 24 Hours De Le Mans with two cars, a stock '49 Coupe de Ville, and another new Cad stripped to the chassis and drivetrain and fitted with a hand-fabbed sports body. The car was unattractive (the French called it "le monstre"), but the stocker came in 10th and the special right behind it. He later installed 331s in a team of Austin-Healey Silverstone sports cars for next year's race. The practice of stuffing hopped-up Cads in specials went on until after 1955 when the smaller, lighter Chevy small-block V-8s were proving their worth.
The Cad as "sleeper" swap material became something of a cottage industry, with the Fordillac and Studillac being the most well-known. Bill Frick had a speed shop and conversion center in New York, and dropped a 331 into his new '49 Ford for towing his race cars. The response from other racers, rodders, and eventually the general public was so strong he started doing this full time. Partnering with racer Phil Walters (aka Ted Tappet), they built and sold at least 200 of these Fordillac conversions, calling the shop Frick-Tappet Motors. When industrialist Briggs Cunningham bought out the shop and took Walters to build his Cad-powered race cars for LeMans, Frick started again alone and specialized this time in installing Cadillac engines into the Loewy-aero Studebakers, which of course he called Studillacs. The Studebaker V-8s shared some dimensions and design features of the Cads, but were only 289 ci and didn't come close to providing the performance that matched the swoopy hardtop and coupe Studebaker bodies. This was no chainfall-from-an-oak-tree operation; Frick had a list of options you could order with your Fordillac or Studillac such as bigger brakes, 12V electrical upgrade, and Hydra-Matic transmission. Despite the three-day conversion costing $1,000-$1,500, Frick sold several hundred Studillacs before Studebaker improved their engine's performance and there was less customer interest.
 If you plan to stuff a Cadillac into the small compartment of a Model A, you'll have to recess the firewall (at left). If yours is a traditional rod with an open engine compartment, it might be easier to just move the radiator and grille shell forward a few inches as seen below.
If you plan to stuff a Cadillac into the small compartment of a Model A, you'll have to recess the firewall (at left). If yours is a traditional rod with an open engine compartment, it might be easier to just move the radiator and grille shell forward a few inches as seen below.
Were they sleepers, you bet! All that Cadillac power under the hood of a "common" car, like a Ford or Studebaker made for a perfect medium for shaming stuffy luxury car owners on an on-ramp, even those with Caddy emblems on their hoods. The production swap cars from Frick-Tappet were offered with chrome Fordillac or Studillac emblems for non-street-racing customers who didn't care about who knew what was under their hood.
Racers also discovered the potential of the Caddys, with these engines showing up in various drag and dry lake cars, and also in a number of high-performance boats, although the list of famous racers using Cads is much shorter than with the Oldsmobiles, which were cheaper to obtain and for which the aftermarket offered much more hard-core speed equipment. You can look through your dusty stack of '50s and early '60s car 'zines and find many a street rod or F-100 pickup featured with high-torque Caddys between the framerails. Iconic rods such as the Kookie T and Roth's Outlaw popularized the Cad's street cred, and by 1957 there were enough really nice examples on the road to prompt Rod & Custom Editor Spence Murray to run a whole section in the magazine on six Cad-powered rods (January 1957).
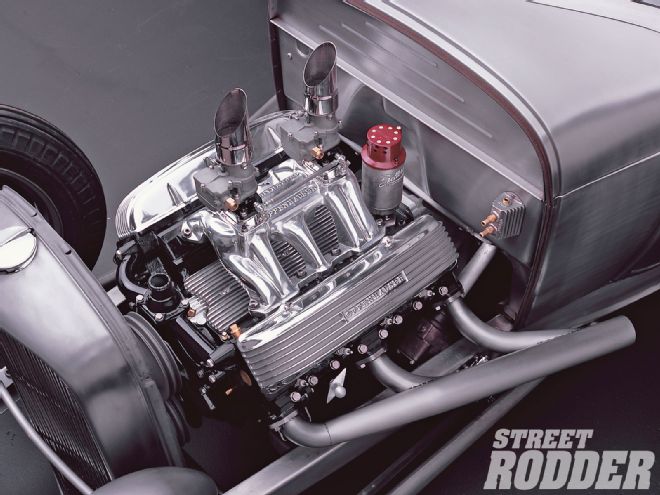
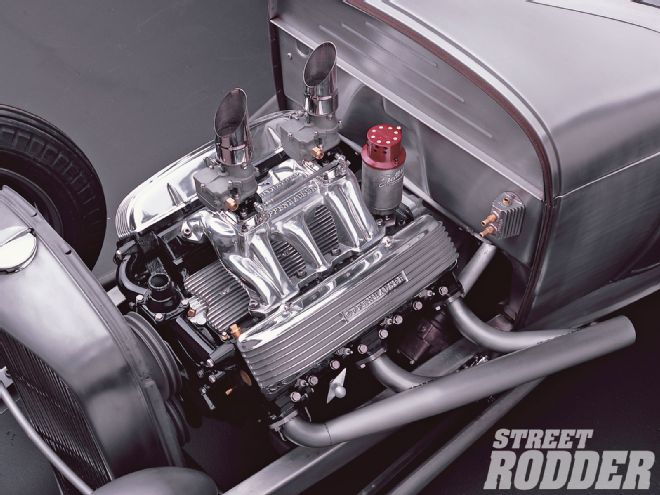
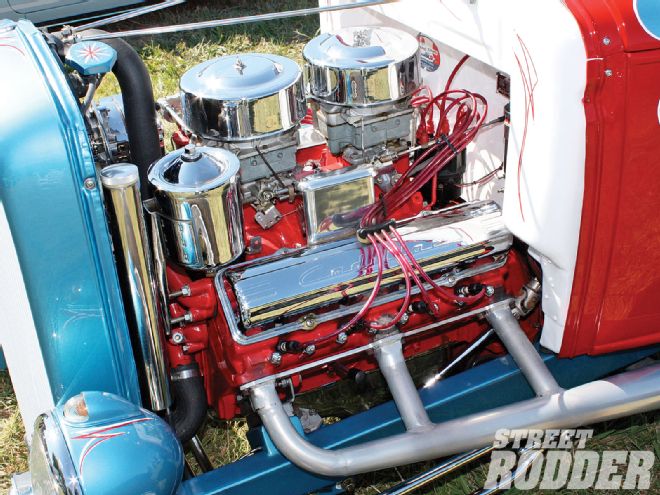
 Compare the location of the oil filter housing on Jim Weems' six-packed Cad to the photo of the stock Cad spot. He moved it to the firewall to better showcase the engine.
Compare the location of the oil filter housing on Jim Weems' six-packed Cad to the photo of the stock Cad spot. He moved it to the firewall to better showcase the engine.
Cadillac engines today
Make no mistake, we are definitely fans of all the pushrod OHV Cadillac engines, including the behemoth 425-, 472-, and 500-inchers of the later years, but for our purposes in this engine series, we're concentrating on the original 331 and its younger brothers, the 365 and 390.
Obviously the 390 engine is the newest of the three Cad engines, and was offered in higher horsepower levels, but all the Cad engines will work great in any size/weight street rod. There is a fair amount of vintage Cadillac speed and dress-up equipment out there at the swap meets, as intakes, cams, finned valve covers, etc., were made in some quantities back then. The Eldorados had factory dual-quad and 3x2 intakes, but they are rare, very heavy iron and today are sought out by restorers. The aftermarket aluminum parts can save more pounds than Jennie Craig. You can still find good aftermarket intake manifolds out there. Edelbrock, Edmunds, Offenhauser (see Exeter Auto Supply), and other companies made them, with many being the 2x2 design, but Offy made 2x2, 3x2, and 6x2 log-type intakes. Luckily, all the engines we're examining take the same intake manifolds.
 If you want to run dual-quads, as some Eldorados were equipped, you'll find intakes at the swap meets, like this Edmunds. You'll have to source out old carbs or use adapter plates to fit later four-barrel carbs.
If you want to run dual-quads, as some Eldorados were equipped, you'll find intakes at the swap meets, like this Edmunds. You'll have to source out old carbs or use adapter plates to fit later four-barrel carbs.
The correct rebuild parts, individually and as kits, are widely available from Egge, Speedway Motors, and other vintage engine parts companies. Any competent engine machine shop should be able to inspect your heads and block for cracks, then deck, bore, and otherwise make true the major surfaces and assemble the engine, leaving you to add the cool stuff you've been gathering from swap meets and eBay. The 390 engines had better breathing heads, and these were commonly swapped onto earlier engines in the old days, although Cads were noted for their grunt rather than high-rpm activities. Cams are available from Iskenderian and SLR Cams. Moon and O'Brien Truckers have finned valley covers, and good old Offenhauser still makes their finned-aluminum valve covers.
The physical dimensions of the Caddy motors are similar to the other vintage GM V-8s we've already looked at, with weight at about 600 pounds and a rear-mounted distributor. Some applications will require a firewall recess to accommodate a Cad, but the end justifies the means. Transmission swaps have already been addressed long ago by our friends at Wilcap, who offer adapter kits for Cads to early Fords, GM automatics, modern GM four-speeds, and a cool setup that allows the use of a small-block Ford bellhousing and a T5 five-speed. Identify your prospective Cad motor by the bellhousing: if the bellhousing is cast in at the back of the engine, it's a '49-54; from '55-62 the back of the block is flat and the trans has the bellhousing. Original Cadillac stick bellhousings are rare and pricey, in fact so are the engines.
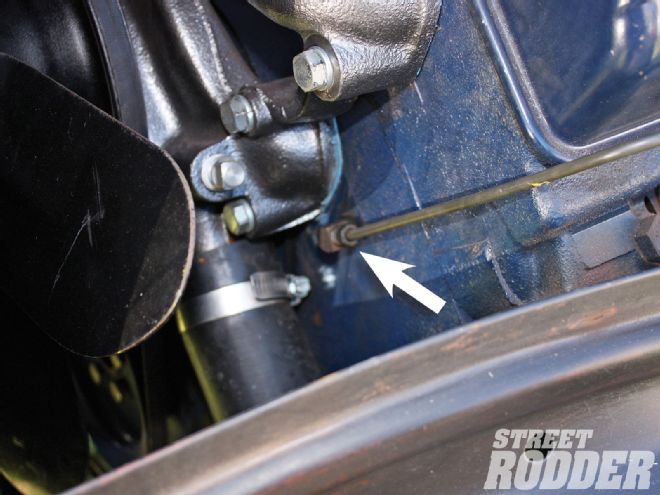 The oil has to flow back into the timing chain area of the engine, so Jim neatly plumbed a copper line to a fitting on the block.
The oil has to flow back into the timing chain area of the engine, so Jim neatly plumbed a copper line to a fitting on the block.
We can't speak for everyone, of course, but all the real motorhead hot rodders we've ever known like to open their hood and show off their engine, and in the old days the engine and engine compartment were often the only detailed and finished part of the rod. Opening your hood at a modern car event and showing off another 350 won't get much attention, but the same vehicle with a Cadillac or other vintage engine will get onlookers approving, talking, and asking questions. Such is the current state of vintage engine interest, and remember the Cadillac slogan: "The standard for the world."