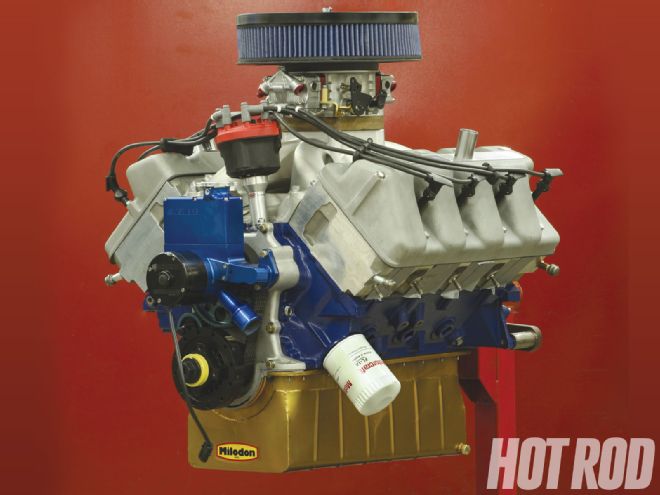

Perception and reality are often widely disparate things. That couldn't be truer than with the legendary Boss 429 Mustang and the semi-hemi engine for which it was named. It is the darling of the Mustang collector world, and the mere mention of its name conjures images of asphalt-annihilating stop-light exhibitions.
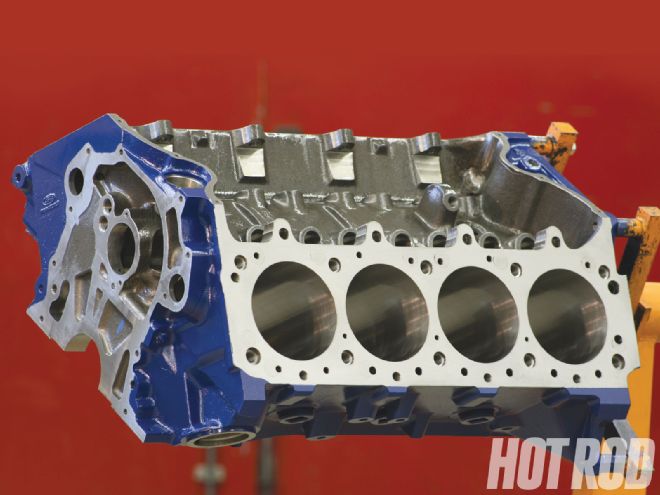 The new Boss '9 build began with a Ford Racing 460 cylinder block, PN M-6010-A460. It's an updated version of the original 385-series block that spawned the original Boss 429, although the original block had four-bolt mains and a denser iron composition when compared with the standard 429/460 design. The block is designed for competition use, so it's stronger than the original blocks, too, and comes with four-bolt mains. A 10.320-inch deck height is standard on the new block and matches the production spec of the original Boss 429 engine. This engine, however, was machined for 4.375-inch bores, which are 0.015 inch larger than the original engine. This delivers a 432ci displacement, but the block can support a displacement of up to 598 inches.
The new Boss '9 build began with a Ford Racing 460 cylinder block, PN M-6010-A460. It's an updated version of the original 385-series block that spawned the original Boss 429, although the original block had four-bolt mains and a denser iron composition when compared with the standard 429/460 design. The block is designed for competition use, so it's stronger than the original blocks, too, and comes with four-bolt mains. A 10.320-inch deck height is standard on the new block and matches the production spec of the original Boss 429 engine. This engine, however, was machined for 4.375-inch bores, which are 0.015 inch larger than the original engine. This delivers a 432ci displacement, but the block can support a displacement of up to 598 inches.
Unfortunately, that wasn't the case-far from it, actually. Like many engines of the muscle car era, the Boss 429 was originally developed as a racing engine, and detuned street versions were typically required for homologation with the racing sanctioning bodies. That meant compromises.
Stuffing the physically massive Boss '9 into the tight confines of the Mustang engine compartment required saddling it with a low-rise intake that effectively choked off airflow to cylinder heads that were way too large for a street engine. Consequently, there was no velocity through the ports, and low-rpm torque was almost nonexistent. Another strike against the engine was a set of crimped exhaust manifolds that were designed to fit the Mustang's engine compartment rather than maximize airflow.
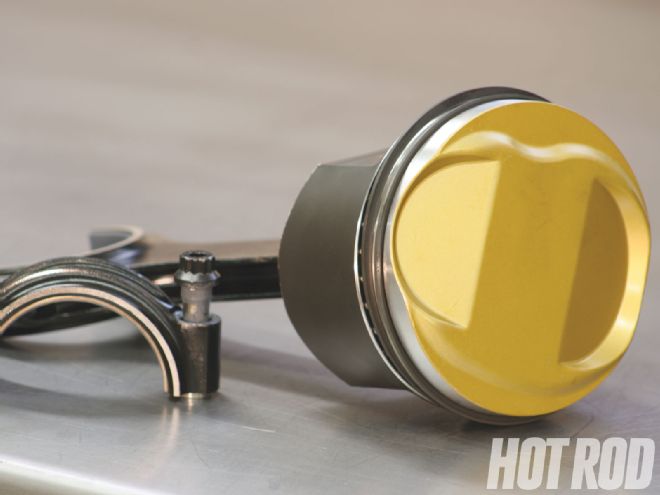 A set of high-temperature-coated, forged-aluminum Diamond pistons pinned to 6.80-inch-long Eagle H-beam rods (also coated) rounds out the rotating assembly. A ceramic coating is used on the head of the piston, giving it a unique gold color. The ceramic coating adds about $25 to the cost of each piston. Friction-reducing Teflon is used on the skirts, which adds a few more bucks to the bottom line.
A set of high-temperature-coated, forged-aluminum Diamond pistons pinned to 6.80-inch-long Eagle H-beam rods (also coated) rounds out the rotating assembly. A ceramic coating is used on the head of the piston, giving it a unique gold color. The ceramic coating adds about $25 to the cost of each piston. Friction-reducing Teflon is used on the skirts, which adds a few more bucks to the bottom line.
To address complaints, Ford instituted a midstream change from an admittedly small hydraulic cam to a hotter solid-lifter setup from the 429 Super Cobra Jet, but it did little to improve the situation. The early hydraulic engines are known by the 820-S engine code, while the later engines are known by the 820-T code (see sidebar). It's true that when wound up, the Boss 429 engine would pull strongly-until the factory rev limiter shut things down. But in most daily driving situations, the Boss 429 was a rather anemic street-performance engine.
On paper, however, the Boss '9 has the potential to deliver big power numbers-if it could only capitalize on its attributes. Engine builders John Lohone and Adney Brown of Detroit-area Performance Crankshaft recently took up the challenge to see what a properly prepared Boss 429 street engine could do when its known deficiencies were addressed. The guinea pig engine belonged to their customer Dave Freelander.
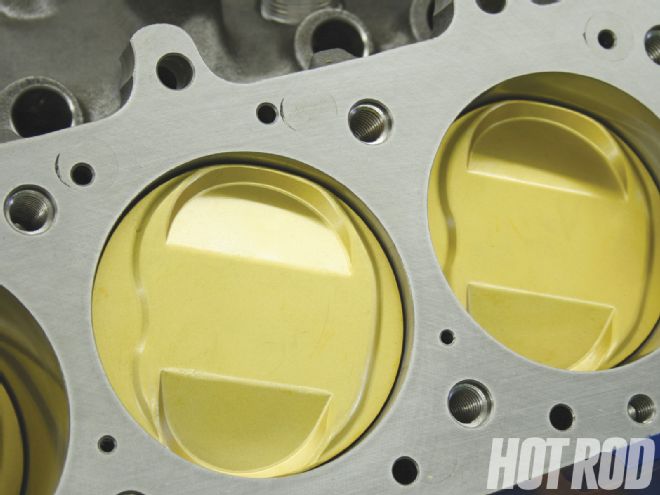 The pop-up configuration of the pistons is evident. It is consistent with the factory piston design, which carried a compression ratio of about 11.3:1. Our project engine had a squeeze ratio of 10.5:1.
The pop-up configuration of the pistons is evident. It is consistent with the factory piston design, which carried a compression ratio of about 11.3:1. Our project engine had a squeeze ratio of 10.5:1.
"We thought if we could take an engine beyond the 600hp level but with good low-speed and idle characteristics, we'd have a great, contemporary combination that's competitive with modern crate engines-but one that's going to elicit some ooohs and ahhhs when the hood is lifted," Brown says.
Brown partnered with Lohone to help develop and assemble the engine, and right away, they knew using an original Boss 429 block and heads was out of the question. The specific, thin-wall casting that is the Boss 429 block is all but impossible to find, and given the collector value of restored cars, it makes the few out there almost as expensive as the investment in this entire project. The same goes for a set of original heads.
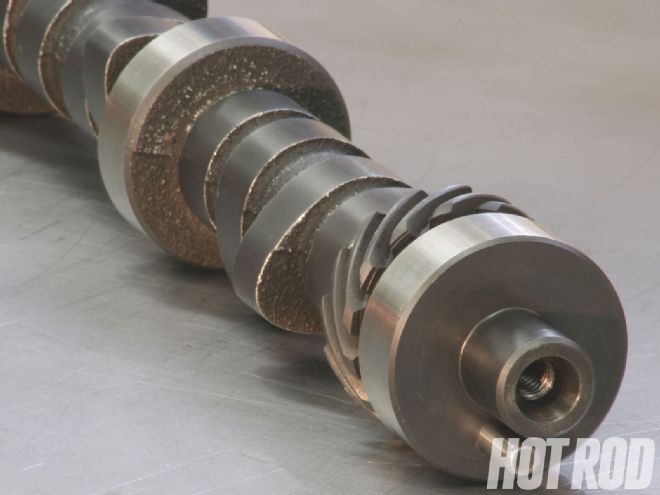 A Comp flat-tappet cam with 0.650-inch lift, 251 degrees of duration (at 0.050 lift), and a 104-degree lobe-separation angle delivered a balance of power and torque in a similar configuration to the original Boss '9, but engine co-builder Adney Brown says a roller cam would have been stronger.
A Comp flat-tappet cam with 0.650-inch lift, 251 degrees of duration (at 0.050 lift), and a 104-degree lobe-separation angle delivered a balance of power and torque in a similar configuration to the original Boss '9, but engine co-builder Adney Brown says a roller cam would have been stronger.
Fortunately, a strong block alternative is available in the Ford Racing catalog with the basic 460 block (PN M-6010- A460). In addition, Ford engine guru Jon Kaase casts his own Boss 429 heads-appropriately named Boss Nine-to fit the 460 block. That's significant because the oiling circuits were different on canted-valve 385-series blocks and the Boss versions, resulting in different oil drain holes. Kaase's heads match the oil drain holes of production-style 429/460 blocks.
Although the project engine uses new parts for the major components, the basic parameters are very similar to the original Boss 429. Therefore, a comparison of the original production engine and this 21st century example is appropriate. In fact, the new engine uses a host of forged, heavy-duty parts, but so did the original engine-including the crankshaft, rods, and pistons.
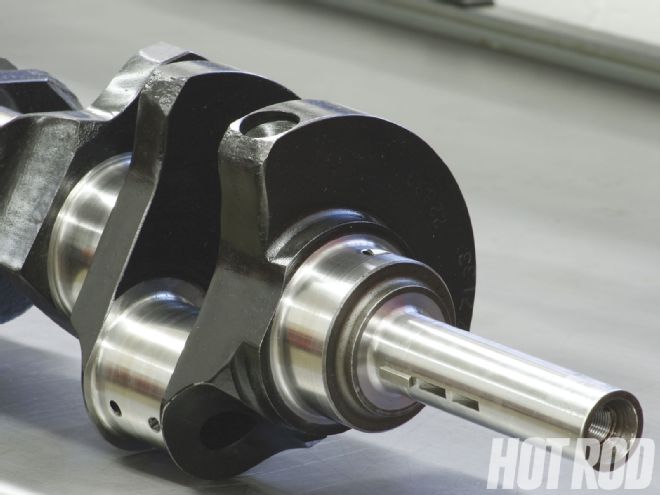 The crankshaft is a forged part from Performance Crankshaft with a stock 3.590-inch stroke. It started life as a 429 truck-engine crank that builder Adney Brown prefers for superior oiling traits over the Boss-style crankshaft. To work on this engine, it was modified and lightened, particularly on the throw sides, and it retains the stock journal sizes. No cross-drilling or other tricks were used on it.
The crankshaft is a forged part from Performance Crankshaft with a stock 3.590-inch stroke. It started life as a 429 truck-engine crank that builder Adney Brown prefers for superior oiling traits over the Boss-style crankshaft. To work on this engine, it was modified and lightened, particularly on the throw sides, and it retains the stock journal sizes. No cross-drilling or other tricks were used on it.
"The bore is a little larger, but the stroke, compression, and basic setup of the engine are very similar to the original," Brown says. "We hoped to make the most of its truly impressive specifications."
The Basics
The Ford Racing 460 block has a 10.320-inch deck height, which is the same as the original Boss 429. The bores were machined to 4.375 inches, and a 3.590-inch-stroke forged crank was used, giving the engine a 432ci displacement. For comparison, the original Boss '9 engine used 4.360-inch bores and the same 3.590-inch stroke. Diamond forged-aluminum pistons are used on the project engine and deliver a 10.5:1 compression ratio that is a little lower than the original engine's approximately 11.3:1 ratio.
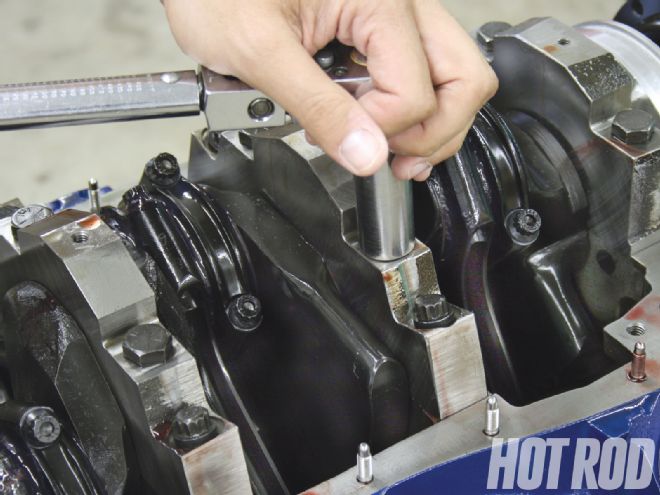 With the engine turned over and the rods and pistons installed, one of the other improvements of the modern Ford Racing block is evident: splayed, four-bolt main caps. Nodular iron caps are standard, but this one is upgraded with stronger billet steel caps.
With the engine turned over and the rods and pistons installed, one of the other improvements of the modern Ford Racing block is evident: splayed, four-bolt main caps. Nodular iron caps are standard, but this one is upgraded with stronger billet steel caps.
The Kaase heads' ports mostly mimic the production Boss 429 design but with subtle improvements that help make them stronger and, of course, fit the 460 block. The biggest difference is the combustion chamber de-sign. The original Ford head got its semi-hemi nickname from a chamber configuration that was based on a true hemispherical design but with filled-in sides that provided better quench. The Kaase head design has a more conventional, fast-burn-style chamber that exhibits more efficient and faster burn characteristics. It is designed to use regular 429/460-style head gaskets. The original heads used individual O-rings around each cylinder instead of conventional gaskets.
Large, 2.300-inch intake and 1.900-inch exhaust valves are used in the Kaase heads-the intakes are only 0.02 inch larger in diameter than the original engines, while the exhaust valve size is the same. Brown and Lohone used a flat-tappet camshaft like later Boss 429 engines to actuate the valves. They specified a Comp Cams grind that delivers a whopping 0.650-inch lift on both sides with 251 degrees of duration also on both sides. That's a huge difference from the 0.478-inch/0.505-inch cam used on the later-style, solid-lifter production engines.
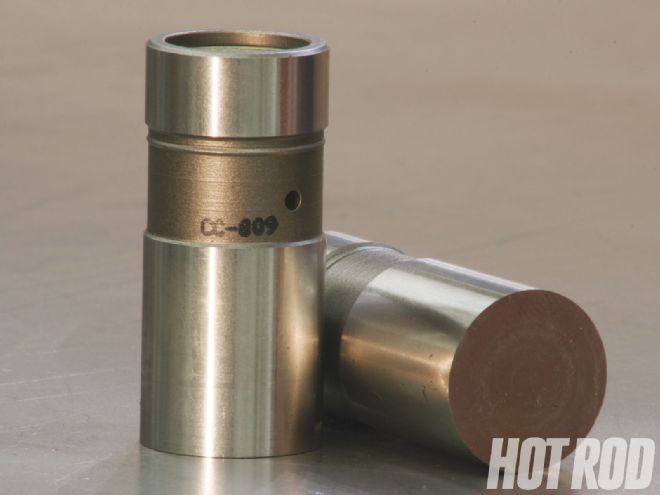 The first 280 Boss 429 engines used a hydraulic cam and lifters, but to answer criticism over their lackluster performance, a solid-lifter setup was used with the later cars. Builders Brown and John Lohone also went the solid-lifter route, using a set of 0.875-inch-diameter Comp Cams No. 809 lifters to match their camshaft.
The first 280 Boss 429 engines used a hydraulic cam and lifters, but to answer criticism over their lackluster performance, a solid-lifter setup was used with the later cars. Builders Brown and John Lohone also went the solid-lifter route, using a set of 0.875-inch-diameter Comp Cams No. 809 lifters to match their camshaft.
As the builders would quickly find out, bigger wasn't necessarily better.
Cavernous Ports
Brown and Lohone discovered that the engine's displacement wasn't enough to satisfy the capability of the cylinder heads.
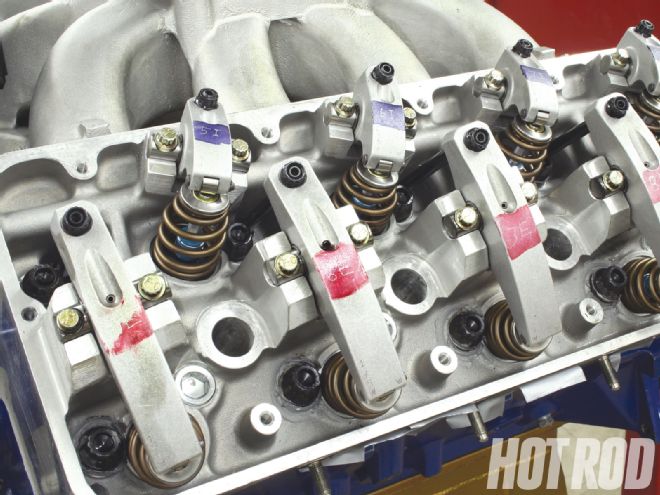 The aluminum heads are from respected Ford engine builder Jon Kaase and are based on the original Boss 429 heads but are cast with some significant changes to make them perform better-and fit the standard 429/460 cylinder block.
The aluminum heads are from respected Ford engine builder Jon Kaase and are based on the original Boss 429 heads but are cast with some significant changes to make them perform better-and fit the standard 429/460 cylinder block.
"The heads are modified when compared with original Ford heads, but they're very similar in design-especially in the intake ports-and we found they're just too darn big for an engine of this displacement," Lohone says. "To build low-rpm power, we cut down the intake runners' volume by about 35 percent, and they still were too big, flowing more than 400 cfm."
It would have been relatively easy to stretch the bore and stroke to accommodate the heads' capabilities, but the project's aim was to build power within the range of the original engine's size. Their experience demonstrated why the factory versions left much to be desired on the street.
"You just can't adequately fill the ports at low rpm with those big heads," Brown says. "What you really need is about another 100 ci of displacement to process what the heads are capable of flowing."
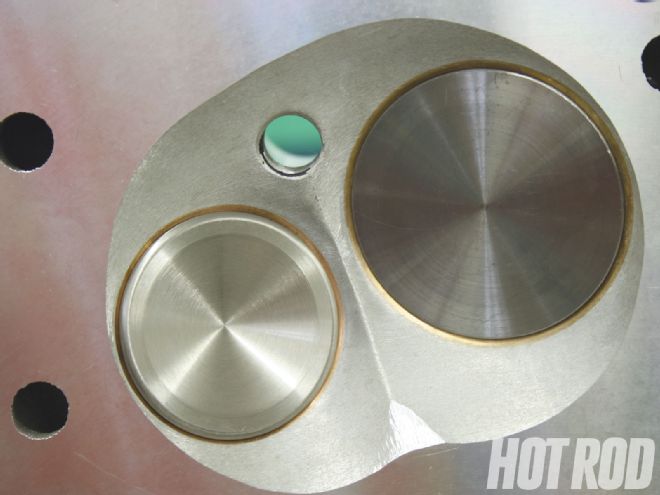 The biggest difference with the Kaase head is the elimination of the semi-hemi combustion chamber design. In its place is a more conventional, fast-burn-type chamber that is more compact than the original design yet still voluminous at 85 cc. A quicker, more complete combustion is achieved with this chamber design, which boosts power. The valve location and valve sizes are essentially the same as the original Boss 429 with the intake valves marginally larger.
The biggest difference with the Kaase head is the elimination of the semi-hemi combustion chamber design. In its place is a more conventional, fast-burn-type chamber that is more compact than the original design yet still voluminous at 85 cc. A quicker, more complete combustion is achieved with this chamber design, which boosts power. The valve location and valve sizes are essentially the same as the original Boss 429 with the intake valves marginally larger.
Despite the challenging combination, the builders achieved eyebrow-raising results after experimenting with a couple of different camshafts and the aforementioned squeeze-down of the heads' intake ports. They topped the engine with a Jon Kaase single-plane, spider-type, high-rise intake manifold (with welded-in wings to effectively lengthen the interior runners), a 1-inch double-tapered spacer, and a 1,050-cfm Quick Fuel-built Dominator-style carburetor. The factory Boss 429, of course, used a lower-rise, dual-plane intake and a much smaller 735-cfm carburetor.
"We even looked at the original NASCAR-style intake, and while it appears impressive, it's totally wrong for a street engine," Lohone says. "It just doesn't flow air at low speed, period."
The velocity afforded by the high-rise intake absolutely benefited the engine at higher rpm, but like the production engine, low-rpm power was relatively weak. During testing, the engine didn't produce 300 hp until 3,500 rpm, although torque was better than 430 lb-ft at only 2,800 rpm. Brown and Lohone experimented with camshafts, header designs, and more on the dyno in a give-and-take learning session that saw peak horsepower and torque numbers vary widely. The best across-the-rpm-range average they saw delivered 670 peak horsepower at 6,400 rpm and 556 lb-ft at 5,600 rpm with 32 degrees of total timing.
"It's a hell of a street engine, no question about it," Lohone says. "From 3,500 rpm to 6,500 rpm, right where you want a street engine to perform, it pulls strong and smooth. It ought to put a '69 Mustang easily into the 10s."
Despite their engine's more-than-respectable performance, Lohone and Brown are left wanting more from it.
"As the dyno results show, there's still a lot left in there-and a roller cam would have easily pushed horsepower past the 800 level," Brown says.
The builders proved their point with this project, realizing much of the potential the original engine packed under its distinctive valve covers. Of course, a 500-inch displacement would be indiscernible from the outside, push output toward the 800hp level, and would arguably have been cheaper to build.
DYNO CHART RPM LB-FT HP 2,800 434 231 2,900 440 243 3,000 445 254 3,100 451 266 3,200 455 277 3,300 459 288 3,400 459 297 3,500 456 304 3,600 455 312 3,700 459 323 3,800 465 336 3,900 471 350 4,000 472 359 4,100 468 365 4,200 466 372 4,300 467 382 4,400 468 392 4,500 472 404 4,600 483 423 4,700 493 441 4,800 506 763 4,900 520 486 5,000 534 508 5,100 543 527 5,200 549 542 5,300 552 558 5,400 553 569 5,500 554 581 5,600 556 593 5,700 556 603 5,800 556 614 5,900 554 622 6,000 553 632 6,100 552 642 6,200 551 651 6,300 551 661 6,400 550 670