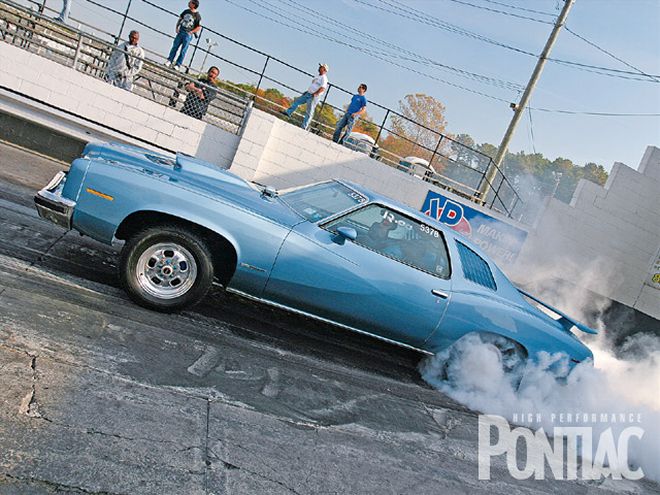


When HPP introduced this engine project to our readers, neither Jim Taylor Engine Service (JTES) nor our staff knew if all of the pains would be worth the results. To recap, customer Bill Wise wanted to upgrade his JTES-built 0.035-over 455 to dip into the 11s after having run a best of 12.54 over the last few years. The challenge was to accomplish this feat knowing it would have to be done in Bill's 4,400-pound race-weight LeMans, while retaining its street manners.
JTES certainly left no stone unturned, with extreme attention paid to the new intake manifold, further porting of the existing 6X heads, and camshaft timing changes, along with the normal high-performance-engine-building acumen. Trying to shave more than a half-second in elapsed time given the restrictions is a major undertaking. What makes this story more exciting is that we have the rare opportunity to follow this buildup from inception to the dyno and back into the car for strip testing.
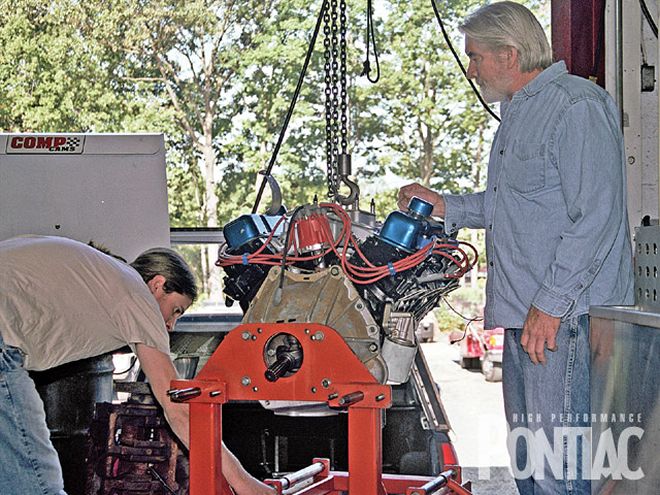 The custom-built 455 was transported to the dyno facility at Bitner Automotive in Trenton, New Jersey. Jim Taylor (right) and Mark Erney carefully removed the powerplant from the back of the pickup truck and mounted it on the dyno cart.
The custom-built 455 was transported to the dyno facility at Bitner Automotive in Trenton, New Jersey. Jim Taylor (right) and Mark Erney carefully removed the powerplant from the back of the pickup truck and mounted it on the dyno cart.
In theory, the engine should produce nearly 500 hp on pump gas. But the dyno cell has often proven the math to be wrong, not only with Pontiac engines, but also with every internal combustion design. The water brake is the real deal, and all the bench-racing talk falls silent when the computer printer spits out the data, like it or not.
Preparation before you leave home is the key to a successful dyno session. Since this engine was run on the JTES test stand, we wouldn't be greeted with a surprise once the dyno loaded the crankshaft. You don't want to find out what's mechanically wrong, if anything, when it's on the dyno. The session is meant to get power numbers on the engine, not repair it.
The Pontiac ran like a champ on Bitner Automotive's dyno and never missed a beat. Idle was smooth, the vacuum signal strong, and the exhaust spoke with authority. The session was remarkably uneventful, which is a testament to JTES.
Did we reach our goal in the dyno cell and on the dragstrip? Well, you'll have to read the rest of the story to find out, but once again a Pontiac did not disappoint.
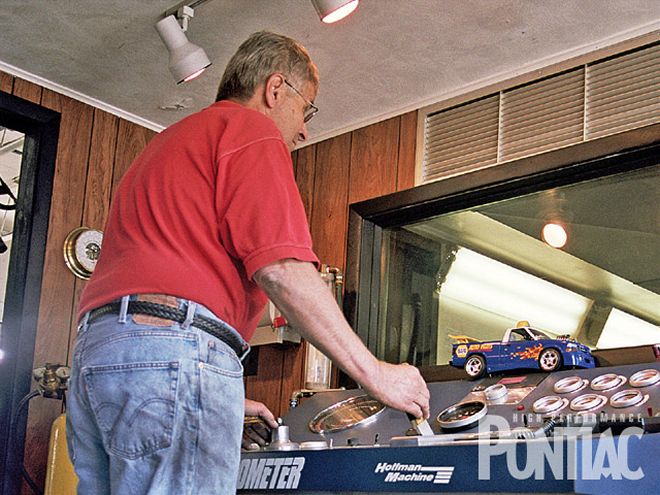 Fred Bitner operated the Hoffman Machine/Stuska dyno during our test session. We made a few part-throttle warm-up runs and then let it rip for a full power pull. On 92-octane pump gas, the engine made 483.7 hp with the Holley carburetor.
Dyno ResultsEach pull was backed up by another to verify the results.Test 1Notes: Jim Taylor Holley 850 DP, No. 83/80 jets, 36 deg timingRPMCorr. HPCorr. Torque4,000371.7501.54,100389.3498.74,200399.7499.84,300411.2500.34,400421.0500.04,500428.3497.94,600437.6496.94,700443.7495.64,800453.2493.94,900461.3494.05,000469.4490.15,100472.9486.25,200475.8477.75,300477.7472.35,400483.7468.15,500483.6461.55,600482.7442.25,700483.5434.75,800481.5427.65,900478.0417.0
Fred Bitner operated the Hoffman Machine/Stuska dyno during our test session. We made a few part-throttle warm-up runs and then let it rip for a full power pull. On 92-octane pump gas, the engine made 483.7 hp with the Holley carburetor.
Dyno ResultsEach pull was backed up by another to verify the results.Test 1Notes: Jim Taylor Holley 850 DP, No. 83/80 jets, 36 deg timingRPMCorr. HPCorr. Torque4,000371.7501.54,100389.3498.74,200399.7499.84,300411.2500.34,400421.0500.04,500428.3497.94,600437.6496.94,700443.7495.64,800453.2493.94,900461.3494.05,000469.4490.15,100472.9486.25,200475.8477.75,300477.7472.35,400483.7468.15,500483.6461.55,600482.7442.25,700483.5434.75,800481.5427.65,900478.0417.0
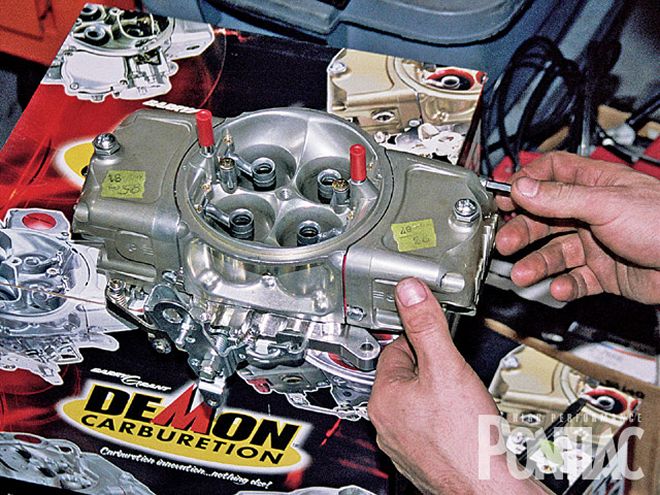 Satisfied with the performance of the engine, Mark Erney switched over to the customer's Demon 850-cfm carburetor. The tune that was in the carburetor was for the engine combo prior to the upgrades. As expected, it was found to be too lean, and the power dropped to 456.5 hp (ignore the jet numbers handwritten on the carb float bowls).
Test 2 Notes: Speed Demon 850, No. 88/94 jets, 36 deg timingRPM Corr. HPCorr. Torque4,000379.4502.24,100392.4501.44,200402.2500.84,300410.8501.24,400420.0499.94,500428.5500.14,600438.4496.94,700444.5495.34,800454.1493.64,900461.8492.55,000467.8490.25,100472.5482.95,200477.2479.95,300479.9474.15,500482.6459.25,600481.2451.15,700483.4443.55,800481.3432.15,900479.3424.26,000476.6416.1
Satisfied with the performance of the engine, Mark Erney switched over to the customer's Demon 850-cfm carburetor. The tune that was in the carburetor was for the engine combo prior to the upgrades. As expected, it was found to be too lean, and the power dropped to 456.5 hp (ignore the jet numbers handwritten on the carb float bowls).
Test 2 Notes: Speed Demon 850, No. 88/94 jets, 36 deg timingRPM Corr. HPCorr. Torque4,000379.4502.24,100392.4501.44,200402.2500.84,300410.8501.24,400420.0499.94,500428.5500.14,600438.4496.94,700444.5495.34,800454.1493.64,900461.8492.55,000467.8490.25,100472.5482.95,200477.2479.95,300479.9474.15,500482.6459.25,600481.2451.15,700483.4443.55,800481.3432.15,900479.3424.26,000476.6416.1
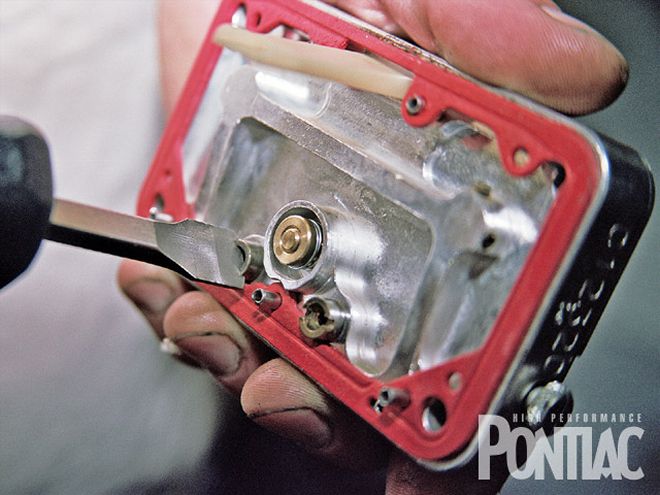 A jet change for the Demon was needed, so the fuel bowls were drained. The carburetor had No. 84 jets in the primary metering block and No. 88 jets in the secondary side. Mark Erney changed them to No. 88/No. 94 primary and secondary, respectively. The performance now equaled the Holley at 483.4 hp.
Test 3Jim Taylor Holley 850 DP, No. 83/80 jets, 36 deg timing, 1-inch Wilson spacerRPMCorr. HPCorr. Torque4,000395.4516.64,100402.4515.14,200410.5512.64,300420.3 512.44,400429.4511.94,500441.5512.54,600449.2512.54,700459.0510.74,800468.3510.54,900473.5505.85,000479.1501.2 5,100485.0497.45,200490.1492.65,300492.7485.65,400494.7 478.85,500496.8472.05,600497.0464.45,700498.5457.75,800500.3451.85,900496.5441.56,000493.6430.4
A jet change for the Demon was needed, so the fuel bowls were drained. The carburetor had No. 84 jets in the primary metering block and No. 88 jets in the secondary side. Mark Erney changed them to No. 88/No. 94 primary and secondary, respectively. The performance now equaled the Holley at 483.4 hp.
Test 3Jim Taylor Holley 850 DP, No. 83/80 jets, 36 deg timing, 1-inch Wilson spacerRPMCorr. HPCorr. Torque4,000395.4516.64,100402.4515.14,200410.5512.64,300420.3 512.44,400429.4511.94,500441.5512.54,600449.2512.54,700459.0510.74,800468.3510.54,900473.5505.85,000479.1501.2 5,100485.0497.45,200490.1492.65,300492.7485.65,400494.7 478.85,500496.8472.05,600497.0464.45,700498.5457.75,800500.3451.85,900496.5441.56,000493.6430.4
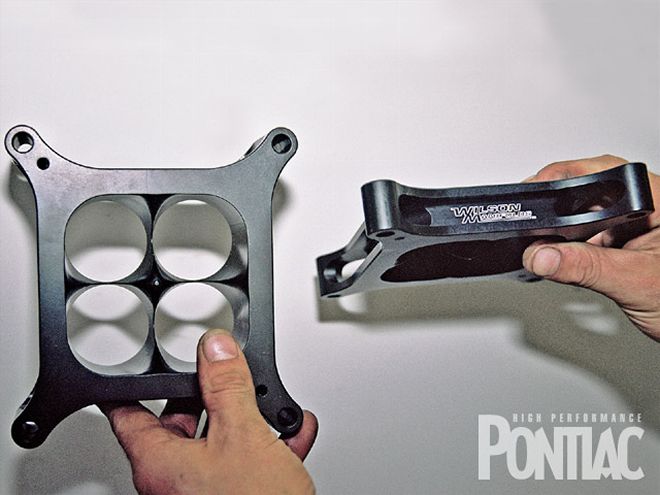 The next step was to try a 1-inch Wilson tapered four-hole carburetor spacer. Jim Taylor decided to go back to his Holley carburetor for the spacer test since the fuel curve was more aggressive than the untuned Demon (we only made a jet change). Wilson claims its spacer will lean the engine out slightly, and since the Holley had No. 83/No. 80 jets, there was plenty of room for tuning with the assortment of parts we brought along.
The next step was to try a 1-inch Wilson tapered four-hole carburetor spacer. Jim Taylor decided to go back to his Holley carburetor for the spacer test since the fuel curve was more aggressive than the untuned Demon (we only made a jet change). Wilson claims its spacer will lean the engine out slightly, and since the Holley had No. 83/No. 80 jets, there was plenty of room for tuning with the assortment of parts we brought along.
High Performance Pontiac
Engine Buildup WorksheetEngine Displacement463ci Bore/Stroke4.185-in bore, 4.210-in stroke Bottom EndBlock Description'73 455Deck Height10.215-inCrank'70-'73 Pontiac nodular-ironBalancerBHJ PO-IB7-SRodsCrower Sportsman forged steel, 6.625-inBearingsSealed Power HDPistonsJE/SRP forged, flat-top with valve reliefsPiston to Deck Height-0.005-inPiston PinsJE full-floating with double spiral locksRingsTotal Seal TS1 gapless, low-tension oil rings (14-lb pull)FastenersCrower connecting rod bolts, ARP head boltsBalancingBy Hoffman Machine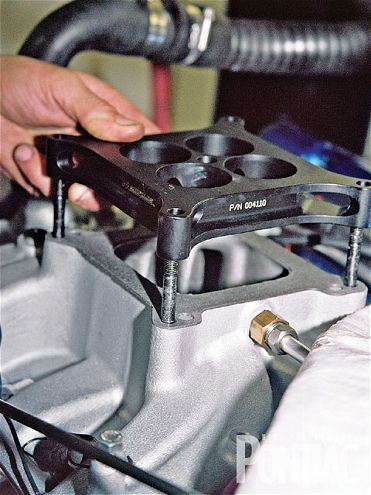 With the Torker II manifold, the engine performed best with the 1-inch Wilson tapered spacer, picking up just under 17 hp and approximately the same amount of torque. The Pontiac now produced 500.3 hp.
Oiling SystemWindage TrayPontiac 455Oil PanMoroso 8-qt Oil PumpMelling M54D, Moroso pickup
HeadsCasting Number6XChamber Open/ClosedOpenHead ModsPortedCombustion Chamber Volume90ccMaximum Flow at 28 Inches of Pressure255/179 cfm at 0.550 inCompression Ratio9.6:1ValvesFerrea SS, 2.11/1.66-inAngles Used in Valve Job30- to 65-deg int, 45-deg exhRetainersComp Cams titaniumKeepersCrower jumbo locks, 10-deg with lash capsValve GuidesK-Line linersValve SealsCorteco all-TeflonRocker StudsARP Pro Series 2-in Rocker ArmsCrower full roller, 1.65 int/1.5:1 exhPushrodsSmith Brothers seamless chromoly 0.083x5/16x9.150-in
With the Torker II manifold, the engine performed best with the 1-inch Wilson tapered spacer, picking up just under 17 hp and approximately the same amount of torque. The Pontiac now produced 500.3 hp.
Oiling SystemWindage TrayPontiac 455Oil PanMoroso 8-qt Oil PumpMelling M54D, Moroso pickup
HeadsCasting Number6XChamber Open/ClosedOpenHead ModsPortedCombustion Chamber Volume90ccMaximum Flow at 28 Inches of Pressure255/179 cfm at 0.550 inCompression Ratio9.6:1ValvesFerrea SS, 2.11/1.66-inAngles Used in Valve Job30- to 65-deg int, 45-deg exhRetainersComp Cams titaniumKeepersCrower jumbo locks, 10-deg with lash capsValve GuidesK-Line linersValve SealsCorteco all-TeflonRocker StudsARP Pro Series 2-in Rocker ArmsCrower full roller, 1.65 int/1.5:1 exhPushrodsSmith Brothers seamless chromoly 0.083x5/16x9.150-in
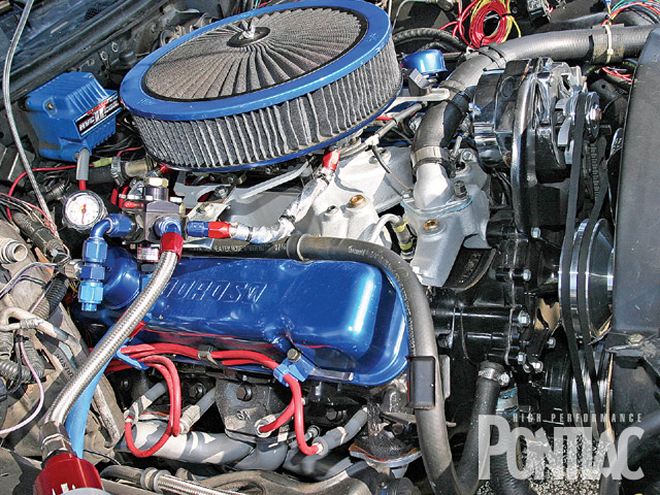 Here's the 463-cube power-plant back in the bay. Even with the A/C removed, the A-body checks in at 4,200-pounds without the driver.
CamBrandCrane solid rollerDuration at 0.050252/256-degLift0.598/0.560 gross, 0.578/0.540 net Lobe Separation Angle112-degInstalled PositionDegreed to cam card by retarding 4 degLifters BrandCrower rollerValvespringsComp Cams dual with damperSeat Pressure165 psiOpen Pressure425 psiTiming ChainRollmaster -0.002-in, double-roller prestreched
Here's the 463-cube power-plant back in the bay. Even with the A/C removed, the A-body checks in at 4,200-pounds without the driver.
CamBrandCrane solid rollerDuration at 0.050252/256-degLift0.598/0.560 gross, 0.578/0.540 net Lobe Separation Angle112-degInstalled PositionDegreed to cam card by retarding 4 degLifters BrandCrower rollerValvespringsComp Cams dual with damperSeat Pressure165 psiOpen Pressure425 psiTiming ChainRollmaster -0.002-in, double-roller prestreched
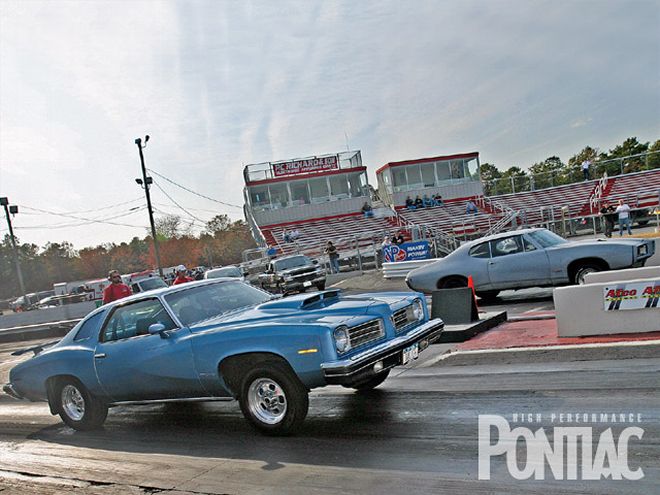 The big heavy LeMans nose comes up on launch as the drag radials dig in.
InductionDyno CarbHolley 850 4781 Dyno JetsNo. 83/80ModsNotched rear float, jet extensionsIntake ManifoldTorker II single-planeModsPort-matched only
IgnitionDistributorMSD Pro-BilletAmplifierMSD 6ALCoilMSD Blaster 2WiresMSDTotal Timing36-deg
The big heavy LeMans nose comes up on launch as the drag radials dig in.
InductionDyno CarbHolley 850 4781 Dyno JetsNo. 83/80ModsNotched rear float, jet extensionsIntake ManifoldTorker II single-planeModsPort-matched only
IgnitionDistributorMSD Pro-BilletAmplifierMSD 6ALCoilMSD Blaster 2WiresMSDTotal Timing36-deg
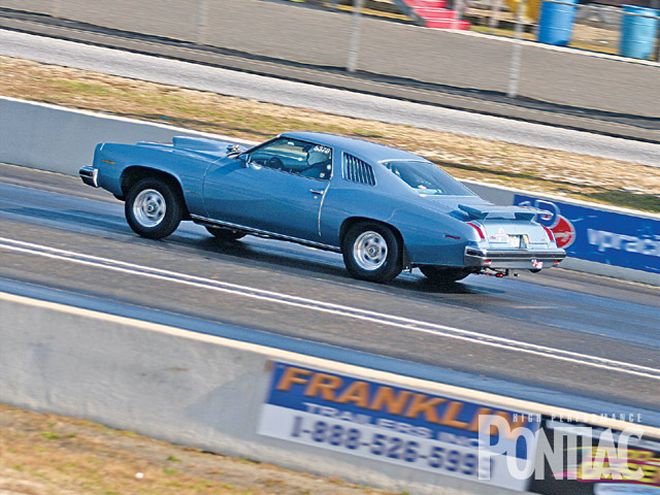 Screaming toward the top end at Atco, the LeMans ran high-11s on this unseasonably warm 70-degree November day at the Pontiac Fall Nats.
ExhaustDyno HeadersHooker 1.75-in primaries, 3-in collectors
Screaming toward the top end at Atco, the LeMans ran high-11s on this unseasonably warm 70-degree November day at the Pontiac Fall Nats.
ExhaustDyno HeadersHooker 1.75-in primaries, 3-in collectors
At The Strip
Once the engine was bolted back in the LeMans, Bill returned to the track. Though the Pontiac was quick at Atco Raceway where we photographed it, the best pass came at Bill's home track--Old Bridge Township Raceway Park in Englishtown, New Jersey. Footbraking to between 1,500 and 2,000 rpm, Bill matted the gas pedal on the last yellow. The 1-2 and 2-3 shifts were made at 6,000, and at the traps the clock showed 11.78 at 113.15. This was a substantial performance improvement.
Engine Changes From The Old Combo To The New
For review, the original 12.54 e.t. combo ran a Demon 850 carb on a JTES-modified Holley Dominator intake manifold, and head flow was 230 cfm.
The new combo runs a Holley 850 DP carb; a Torker II intake with a port match; a Wilson 1-inch carb spacer; the flow of 6X heads has been increased to 255 cfm; the pistons were thermal-barrier-coated by Swain Technology; and the block was partially filled with Rokblock. The same cam was retained but was retarded 4 degrees using an offset cam key.
 Screaming toward the top end at Atco, the LeMans ran high-11s on this unseasonably warm 70-degree November day at the Pontiac Fall Nats.
Screaming toward the top end at Atco, the LeMans ran high-11s on this unseasonably warm 70-degree November day at the Pontiac Fall Nats.
Bear in mind there are also some differences between the dyno combo and the in-car combo. Bill decided to get a Holley 850 DP like the dyno carb, and it's set up similar to it, but jet changes are made to suit weather and track conditions. Though the headers are close to the same configuration as the dyno set, Bill's street car runs a full exhaust system that's not uncorked at the track. Compared to the dyno, in the car, the engine breathes through an air cleaner, drives accessories, and uses a different fuel system.
’74 LeMans Sport Strip SpecsAncillary Engine ComponentsAir CleanerK&NCarburetor850 DP set up like dyno carb JetsNo. 82/84 at track SpacerWilson 1-in aluminum taperedFuel PumpMallory 140Lines-10 from tank with sump, -8 to reg, -6 to carbRegulatorMallory set at 7 psi HeadersHooker 1.75-in primaries, 3-in collectorsExhaustKooks 3-in x-type pipe, Spintech mufflersTiming36-deg DrivetrainTransmissionFord AOD, done by FB transmissions in Long Island, NY; SFI bellhousing to mate Ford trans to GMConverterPro Torque 10-in, 3,500, (flash to 3,800 rpm)ShifterB&M Pro RatchetRearFactory 8.5-in, 3.90:1 gears, Detroit locker, Mark Williams axles Chassis and SuspensionBrakes F/RSSBC caliper, slotted 11-in rotors/stock drum, ABS Power Brakes master-cylinder electric accumulatorWheels F/RWeld Rodlite 15x6/15x8Tires F/RGoodyear Aquatred 215/70R15/M/T 275/60-15 Drag RadialsTire Pressure F/R35 psi/20 psiSuspension FrStock with 90/10 drag shocksSuspension RrDick Miller Racing bolt-on 4-Link, pinion set at 2.5-deg neg., adj QA1 set at 3 softChassis ModsSix-point barConclusion
Was this project successful? The 12.56 e.t. 4,400-pound LeMans now runs 11.78. According to Bill, "I feel a big difference in power on the track and on the street, but it drives like a stocker around town. It idles well and doesn't run hot. I feel like I could drive this car across country." Sounds like Bill got what he desired from the new JTES combo. Follow the plan outlined here and you can, too.