
We'll go out on a limb here by saying that in the coming years, the Gen III small-block will become the dominant engine in performance engine circles. Eventually, this small-block family will overshadow even the original small-block Chevy juggernaut. That time is coming, friends, and for good reason.

Last month we outlined many of the details required to get one of these latest-generation factory small-blocks running on the dyno, which is the same situation you'll face when you bolt one of these engines into an early musclecar. Last month's baseline revealed the engine made 402 hp at 5,700 rpm and 398 lb-ft of torque at 4,300 rpm just as it rolled out of the box. Then we removed the engine to make way for a series of thumper race engines on Duttweiler's Digilog dyno. Once our LS1 was back on the pump, we baselined the engine again before proceeding with this month's header test.
If you refer to last month's dyno run, you can see that this exact same engine running on the same dyno with the exact same parts, did not make exactly the same power. We've discussed this with our pal Steve Cole at The Turbo Shop (TTS) and the power difference we witnessed relates, in part, to removing the electrical power from the computer. This clears the memory, and the computer must then start from scratch in terms of trimming the power as the tests continue. We mention this just as a point of reference to help you see how complex the procedure is when testing these new engines on an engine dyno.
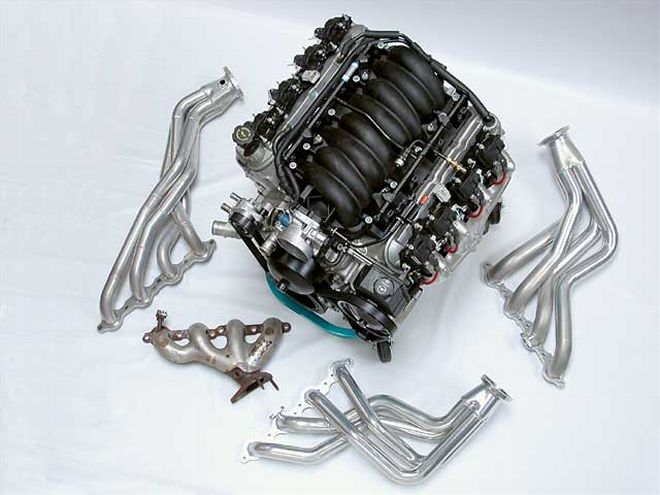
The GM Performance Parts LS1, that our friends at Scoggin-Dickey Performance Center in Lubbock, Texas, are helping us test, comes in an interesting configuration. According to our pals at GM Performance Parts, this engine is actually a GTO engine, but it comes with an F-car (Camaro/Firebird) oil pan and Corvette-configured exhaust manifolds. The exhaust manifolds became a very important consideration once we started our dyno-testing.
Manifold Destiny
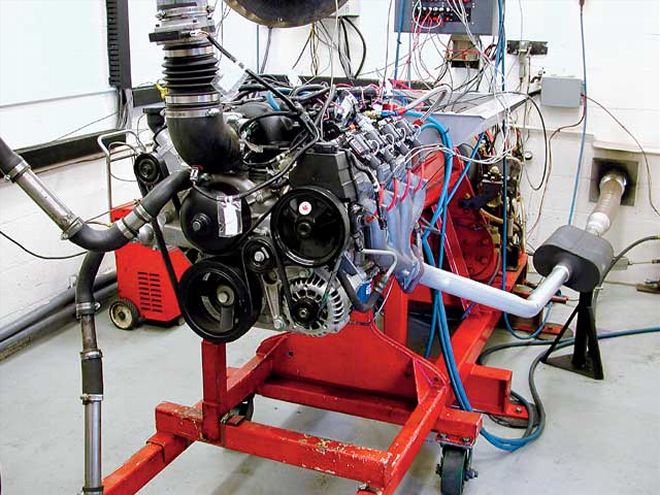 Here's the Scoggin-Dickey LS1 in Duttweiler's recently overhauled dyno cell. Note that all Car Craft tests on this engine are configured with a complete front dress assembly with only the A/C compressor missing. All our tests also included a complete exhaust system with a pair of Flowmaster mufflers.
Here's the Scoggin-Dickey LS1 in Duttweiler's recently overhauled dyno cell. Note that all Car Craft tests on this engine are configured with a complete front dress assembly with only the A/C compressor missing. All our tests also included a complete exhaust system with a pair of Flowmaster mufflers.
We started by rebaselining our LS1, which generated 396 hp at a somewhat high 6,100 rpm and a torque peak of 391 lb-ft at 4,900. With virtually every production engine we've ever tested, the first thing you can do to gain power is to throw on a set of headers. Steve Cole at TTS volunteered a set of 1 5/8-, 1 3/4- and 1 7/8-inch headers to try across our stock Gen III engine. It's important that we mention that TTS doesn't offer 1 5/8-inch headers for either a Corvette or a late-model Camaro. But since we wanted to see what the headers could do, Steve created a set especially for our test.
We really thought the 1 5/8-inch headers would work best, because our Light Speed LS1 was stone stock. But we should have known that Steve's been around awhile and his knowledge base on these Gen III engines is extensive. So our first comparison was with the 1 5/8-inch headers versus the Vette iron manifolds. We did not include a full dyno comparison of these headers, because you can see from the peak numbers that this smaller header ran acceptably against the stock Vette manifolds. However, the average torque and horsepower numbers are actually very close. The headers enjoyed a larger 2 1/2-inch exhaust pipe compared to a compression-bent 2 1/4-inch system for the iron manifolds, and the Flowmaster mufflers remained the same for all the tests. Hmmmm....
We decided to test the next larger set of 1 3/4-inch TTS headers to see how well they performed. This time, the numbers were a bit more rewarding. These larger headers only equaled the horsepower of the iron Vette manifolds, and the peak torque was up 5 lb-ft, the average torque (which is the real key to any comparison) increased slightly, yet average horsepower was up negligibly.
Next, our intrepid dyno-tester Ed Taylor bolted on a set of 1 7/8-inch headers, which would seem on the surface to be much too large for a stock engine at this horsepower level. Once again, we're learning that the LS1 is a different animal. Average torque and horsepower increased marginally, yet we made the highest peak power level of 402 hp-up 6 hp over the best the 1 5/8-inch tubes and the iron Vette manifolds made.
The amazing performance of the stock iron Vette manifolds prompted us to test a set of iron F-car manifolds, which are significantly different from the Vette pieces. Here, the performance was dramatically down, dropping an average 9 hp, 9 lb-ft of torque, and 12 peak horsepower compared to the Vette manifolds. Clearly, there is a significant difference between the two iron manifolds. If the Vette manifolds will work in your chassis, there's much to be said for these off-the-shelf pieces.
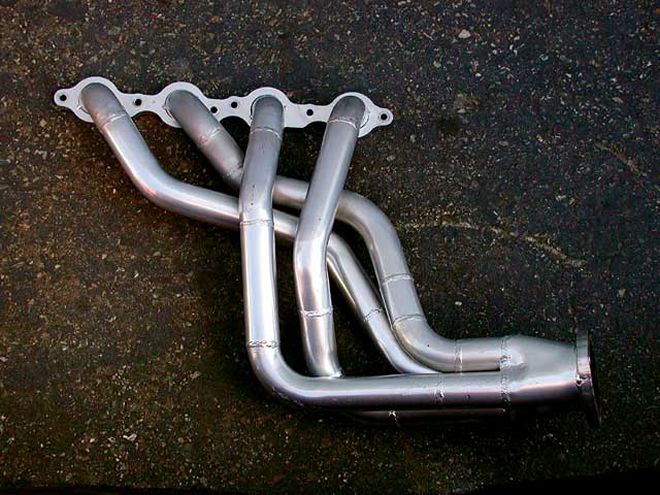 The Turbo Shop (TTS) supplied the headers for our test. They don't make a production set of 1 5/8-inch headers for a late-model Camaro, but they whipped up a custom set for us. Our testing revealed why TTS chose not to build these smaller headers!
The Turbo Shop (TTS) supplied the headers for our test. They don't make a production set of 1 5/8-inch headers for a late-model Camaro, but they whipped up a custom set for us. Our testing revealed why TTS chose not to build these smaller headers!
Evaluation
So what did we learn from this exhaustive flog-fest? First, the Vette manifolds for a stock LS1 even at the 400hp level, are extremely efficient. We learned that larger primary pipe tubes tend to work well on a stock LS1, which leads us to think they will work even better on a modified engine with a better cam and heads. There is data to support the notion that longer primary pipe lengths approaching 40 inches plus a longer collector length may be worth more torque. Generally, we'll see torque improvements with a longer collector, but these TTS headers were designed to fit in a late-model F-car as opposed to perhaps a first-gen Chevelle or Camaro where there would be more room for a longer collector and primary pipe lengths.
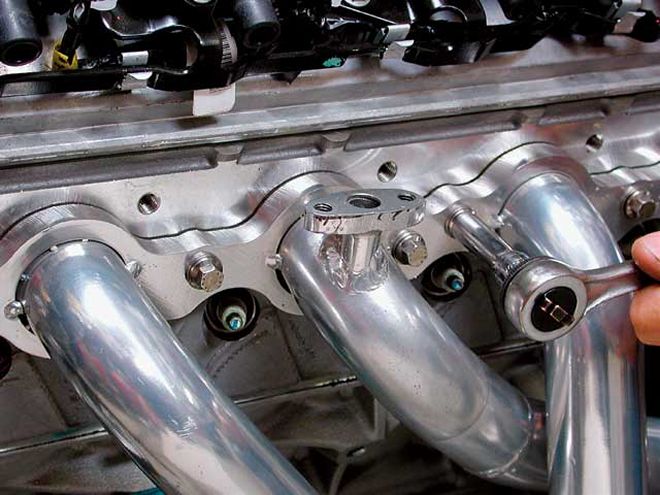 The TTS headers feature extremely thick 1/2-inch flanges to prevent warping, so all we had to do was bolt them on using ARP's metric header bolts.
The TTS headers feature extremely thick 1/2-inch flanges to prevent warping, so all we had to do was bolt them on using ARP's metric header bolts.
The bottom line is that a stockLS1 can obviously make as much as 400 hp using stock Vette iron exhaust manifolds, so don't toss those Vette pieces in the trash! It is also clear that the right size headers can still improve power on one of these engines with the right combination of parts.
Stick with us as we look into the best ways to make more power with our GM Performance Parts LS1. The idea here is to make power without resorting to spending a ton of money. We want to make this LS1 sing for a song.
2,600
348
172
348
172
—
—
348
186
351
187
+3
+1
351
201
351
201
—
—
363
221
363
221
—
—
363
235
364
236
+1
+1
371
254
375
257
+4
+3
374
271
373
270
–1
–1
386
294
379
288
–7
–6
385
308
390
312
+5
+4
389
326
396
332
+7
+6
387
339
389
340
+2
+1
390
356
393
359
+3
+3
390
371
395
376
+5
+5
385
382
389
385
+4
+3
381
392
378
388
–3
–4
367
392
370
394
+3
+2
356
393
364
402
+8
+9
6,000 339 387 346 396 +7 +9