

It's no secret that the new Gen III small-block is the hot engine in the performance aftermarket. Everyone has been stuffing cams and manifolds into 5.7Ls and some have even experimented with those expensive Gen III-based 427ci engines. We're planning to do our own 5.7L LS1 dyno engine buildup, but because this is Car Craft, we thought we'd start off a little differently.
Last month, we ran a story on how all the 4.8, 5.3, 5.7, and 6.0L engines offer tremendous interchangeability ("The New Generation," pg. 72, Sept. '04). Of these four, the 5.3L (325ci) truck powerplant is by far the most prolific, used predominantly in midsized pickups since 1999. That means it won't be long before this iron block, aluminum-headed small-block is filling the wrecking yards. We decided that this little engine deserved a little attention-along with a couple of camshafts, some ported cylinder heads, and an intake or two all under the careful attention of the guys at Lingenfelter Performance Engineering (LPE).
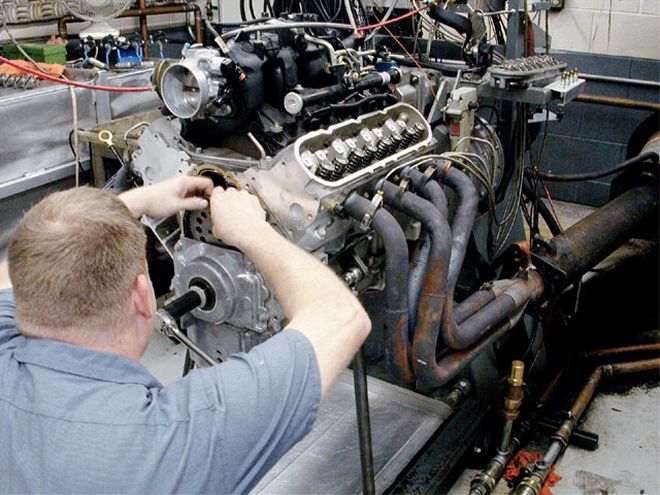
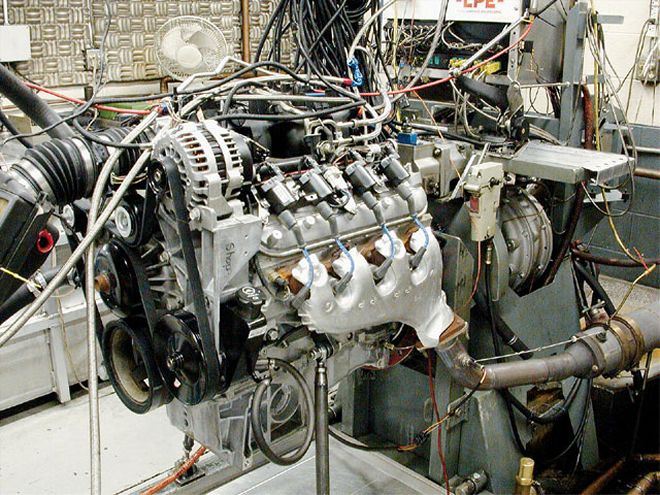 After Rob "Dyno Bob" Vanderhart bolted the stock SSR 5.3L engine on the dyno at Lingenfelter's, we began by baselining the engine completely stock including iron exhaust manifolds and the equivalent of a full exhaust system.
After Rob "Dyno Bob" Vanderhart bolted the stock SSR 5.3L engine on the dyno at Lingenfelter's, we began by baselining the engine completely stock including iron exhaust manifolds and the equivalent of a full exhaust system.
It should be common knowledge that our friend John Lingenfelter passed away in December of 2003. But his performance legacy continues to thrive in the Decatur, Indiana, business that he began over 30 years ago. General Manager Tom Cress and Project Director Jason Haines are just two of the many people still very much involved in cranking out powerful LPE street and race engines. Since LPE has such a distinguished performance record with these Gen III engines, we asked them if they'd be interested in aerobicizing a 5.3L. Cress immediately suggested that we step it up and do the all-aluminum 5.3L that's in the current Chevy SSR truck. LPE offers these brand-new engines for a decent price and it sounded like an outstanding idea. The plan for this month would be to test headers and a couple of camshafts to see how much power we could make. Next month, we'll add a set of LPE CNC-ported heads, and one of Comp Cams' LSXtreme intakes to see where those mods take this little 5.3. But that will have to wait until next issue.
Power Add-Ons
The production 5.3L SSR engine is a virtual clone of the iron block version except for its aluminum block, yet GM rates the SSR 5.3 at a healthier 300 hp and 330 lb-ft of torque using the SAE production car correction factor that employs a higher inlet air temperature (and other changes) that explains why the SAE corrected numbers are always lower. LPE's Rob "Dyno Bob" Vanderhart bolted the bone-stock 5.3L SSR engine to the dyno along with a complete accessory drive on the front of the engine as well as the equivalent of a muffled exhaust system connected to the stock iron exhaust manifolds. The LPE baseline in this configuration used the traditional and more lenient aftermarket correction factor and generated 313 hp and 345 lb-ft of torque, which is right in line with the factory specs assuming a 5 percent differential between the two correction factors. There may even be the advantage of a few extra ponies with an iron block compared to the aluminum version.
Exhaust work and headers are always a good place to start, so Dyno Bob bolted on a set of Hooker 131/44-inch dyno headers. Since the motor is only 325 ci, these are a little bigger than would probably be best on the street, but they were the best headers available at the time of the test because most of LPE's work is with larger and more muscular LS1s. Even with the slightly larger headers and street exhaust, the header swap was worth reasonable power throughout the entire curve.
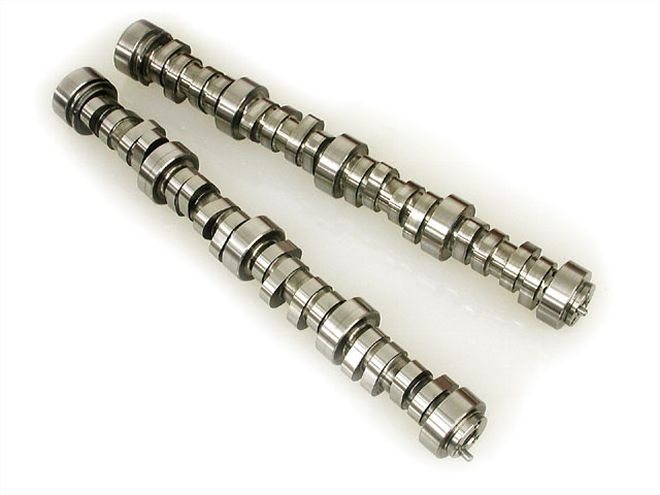 We decided to test two different cams, both LPE grinds. The milder of the two will work in an emissions application yet still bumps the stock lift by 0.115 while the larger of the two cams kicks the lift up to a stout 0.631 inch.
We decided to test two different cams, both LPE grinds. The milder of the two will work in an emissions application yet still bumps the stock lift by 0.115 while the larger of the two cams kicks the lift up to a stout 0.631 inch.
Cam It Up
Some may suggest at this point that we add a performance-style intake. According to the guys at LPE, their testing has shown that despite the truck manifold's pedestrian image, it's a great manifold, so we instead decided to bolt in a camshaft. The first cam is what LPE calls its GT2-3 cam, which is mild enough to generate a stock idle (20.7 inches of vacuum at 800 rpm) yet pumps the lift and duration up substantially (see the Cam Specs chart) by adding 0.115 inch of lift on the intake side alone! This is still using the stock 1.7:1 Gen III shaft rocker arms. Since we were adding a more aggressive camshaft to the mix, Dyno Bob also swapped the stock beehive springs for a set of Comp Cams performance LS1 beehive springs just to handle the additional lift and rpm.
One of the great things about the Gen III small-block is how easy it is to swap cams. Dyno Bob removed the rocker shaft and pushrods, pulled the accessory drive and balancer off, and then yanked the timing cover and cam gear. If you spin the engine over two revolutions with the rockers and pushrods off before removing the cam drive, the lifters will sit up out of the way so the cam can be removed without pulling the intake! The biggest hassle is properly positioning the timing cover and tightening the stock torque-to-yield balancer bolt.
Since all Gen III engines come with hydraulic roller cams, we even reused the stock hydraulic roller tappets, making a cam swap even more affordable. LPE decided to also add a Cloyes adjustable timing set to the engine in case we wanted to move the cam around, but for this test, we left it dialed in straight up. Looking at the dyno numbers, this first camshaft gave up a little torque below 2,600 rpm, but added an astounding 76 hp at 5,800 rpm! This combination pushed the peaks up to 378 hp at 6,000 and 366 lb-ft of torque at 4,800 rpm. If you compared the horsepower peaks, this little cam was worth 65 hp over the stocker while also adding 21 lb-ft at peak torque. Keep in mind that all we've done is bolted in a conservative camshaft, a set of Comp valvesprings, and a set of 131/44-inch headers.
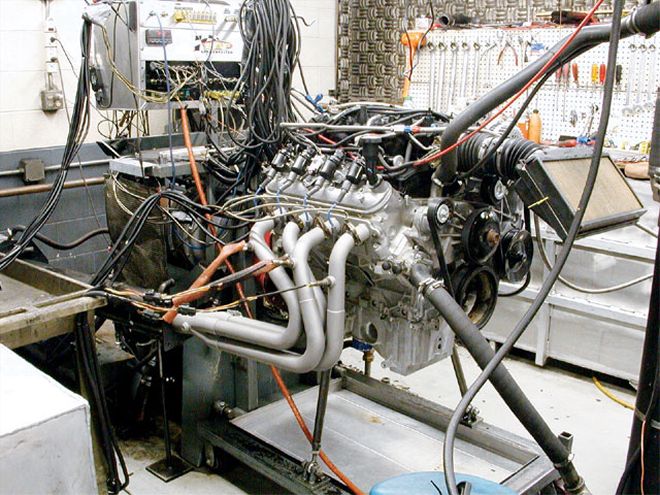 The first and simplest modification involved merely bolting on a set of 131/44-inch headers. Ideally, this engine might have made even more torque and similar horsepower with a set of 151/48-inch headers, but the larger pipes were all we had.
The first and simplest modification involved merely bolting on a set of 131/44-inch headers. Ideally, this engine might have made even more torque and similar horsepower with a set of 151/48-inch headers, but the larger pipes were all we had.
Now it was time for the big camshaft. This time, LPE pulled out a much more aggressive mix of lobes that most certainly will qualify it as "fairgrounds lumpy." This is LPE's GT1-1 cam that bumps the duration at 0.050 up to 229/242 degrees of duration while the valve lift skyrockets to 0.631 inch for both intake and exhaust. That's 0.175 inch more lift than the stock cam! While this is a big cam for a little 325ci engine, it also promised some healthy horsepower numbers. Dyno Bob again went through the drill of swapping cams, which he accomplished in less than an hour. After he brought the engine back up to temperature, the cam's more aggressive nature showed up with 10 inches of manifold vacuum at its 900-rpm idle speed.
After several power pulls, it was obvious that we had traded low-speed torque for horsepower since the big cam created quite a torque dip between 2,000 and 3,500 rpm where the motor lost as much as 50 lb-ft at 2,400 rpm. This is typical of a big cam with lots of overlap. The power almost overlapped the original stock engine's level between 3,000 and 4,200-then the big cam began to make some serious noise. From 4,400 to 6,800, this little small-block rocked! Peak horsepower jumped to 413 at 6,600 while torque peak settled in at 369 lb-ft at 4,800 rpm. This also created an 1,800-rpm power spread between peak torque and peak horsepower. Remember, this is still with the stock truck intake, throttle-body, and stock heads!
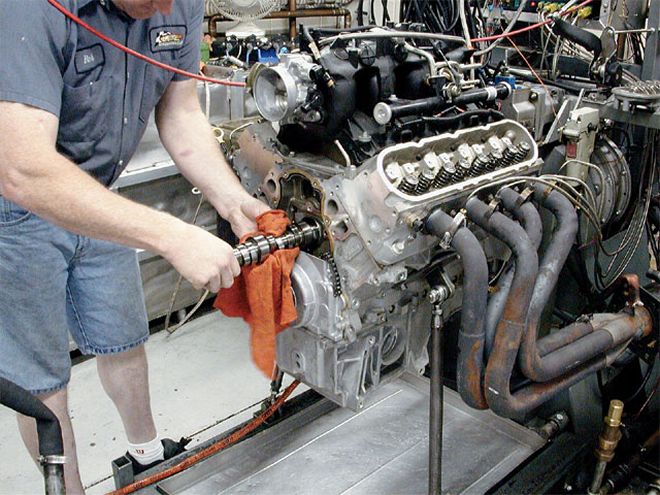 Installing a cam in a Gen III engine is made easier because you don't have to pull the intake manifold. Dyno Bob made his own two-piece timing cover to make these swaps easier.
Installing a cam in a Gen III engine is made easier because you don't have to pull the intake manifold. Dyno Bob made his own two-piece timing cover to make these swaps easier.
So with the addition of a set of headers and an admittedly lumpy cam, we've managed to add an even 100 hp to our Little Bro 5.3L motor. This doesn't come without a price, however. We've pushed the torque peak from 4,000 rpm to 4,800 and lost a bunch of torque below 3,000. But baby, when the tach hits 4,000, this motor will feel much more like a healthy 350 instead of a little 325! At 413 hp, this equates to 1.27 hp per cubic inch (hp/ci), all with stock heads.
But the story's not over. Next month, we'll lay on the LPE CNC-ported heads, and a Comp Cams LSX intake to really pump up the LS1's little brother. As a teaser, think about how much pump gas power equals 1.4 hp/ci.
What's A 5.3?
Everybody knows what an LS1 5.7L motor is and how much power it makes. But fewer seem to know the details around its 5.3 little brother. Basically, GM just made the bore smaller (3.780) and kept the stroke the same (3.622). All other parts interchange, just like the Gen I small-blocks. The 5.3L is used most often in 11/42-ton pickups and vans and has come in horsepower ratings from 265 to 300 hp while torque ranges from 320 to 330 lb-ft depending on its application.

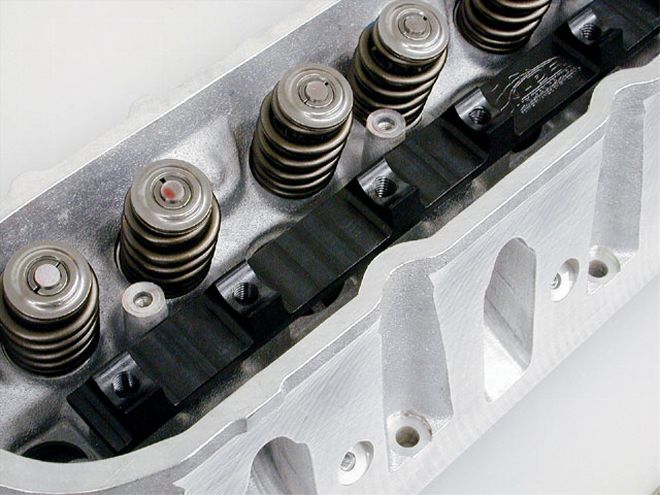
The 5.3 heads are very similar to those used on the LS1, but the chambers are smaller to keep the compression up and the intake valves are 1.89-inch instead of the larger 2.00 for LS1s. Exhaust valves are the same as the LS1 at 1.550 inch.
The easiest way to think of this engine is as a small-bore 327. The bore is 0.220 inch smaller than the original 327, making up the difference with its longer 3.622-inch stroke that is the same as the 5.7 LS1 along with the same rod length. Even the stock heads exhibit exceptional flow and there's probably some power to be had by minor pocket work as opposed to the full-on CNC porting. All this makes for an excellent mid-displacement street engine.
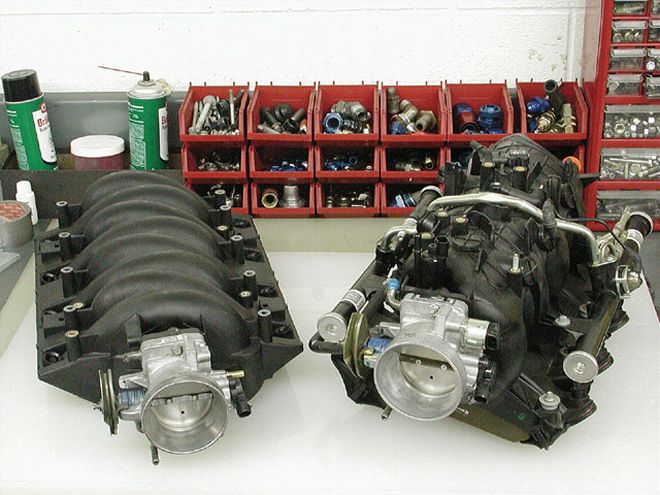
 We used the stock truck intake (right) for all the tests in this story. On the left is an LS6 intake used in the Corvette that is worth some power, but only in the upper rpm range. The stock truck intake may not look as pretty, but it worked very well on our Lil' Bro 5.3 making 413 hp!
Cam Specs Camshaft Advertised Duration Lift Lobe Duration @ 0.050 (inches) Sep. (0.006-inch) Stock 5.3L Int. 259 190 0.456 114.0 Hyd. Roller Ex. 259 190 0.464 LPE GT2-3 Int. 255 206 0.571 118.5 Hyd. Roller Ex. 282 221 0.578 LPE GT1-1 Int. 276 229 0.631 114.5 Hyd. Roller Ex. 303 242 0.631
We used the stock truck intake (right) for all the tests in this story. On the left is an LS6 intake used in the Corvette that is worth some power, but only in the upper rpm range. The stock truck intake may not look as pretty, but it worked very well on our Lil' Bro 5.3 making 413 hp!
Cam Specs Camshaft Advertised Duration Lift Lobe Duration @ 0.050 (inches) Sep. (0.006-inch) Stock 5.3L Int. 259 190 0.456 114.0 Hyd. Roller Ex. 259 190 0.464 LPE GT2-3 Int. 255 206 0.571 118.5 Hyd. Roller Ex. 282 221 0.578 LPE GT1-1 Int. 276 229 0.631 114.5 Hyd. Roller Ex. 303 242 0.631
Test Results
Test 1:
This was our baseline test of a totally stock 5.3L all-aluminum SSR truck engine, complete with the stock exhaust manifolds running through a typical performance dual exhaust system.
Test 2:
The only change was to add a set of 131/44-inch dyno headers to the engine with the same exhaust downstream. This change was worth about 10 lb-ft of torque and 10 hp over the cast-iron manifolds.
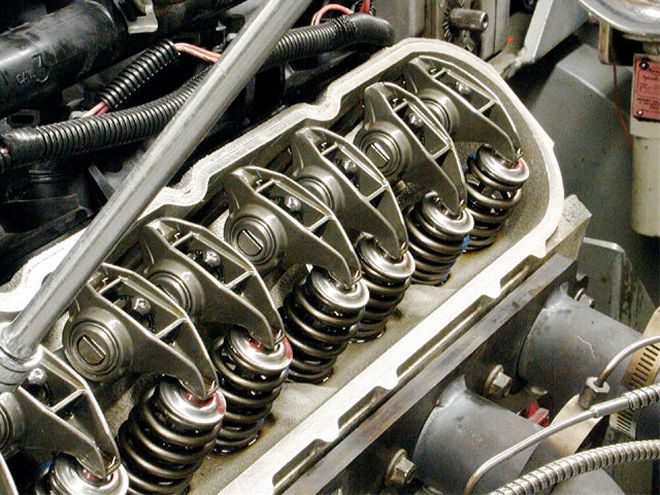 LPE also offers a steel rocker arm stand that locates the rocker shaft assembly and replaces the somewhat fragile stock aluminum piece.
LPE also offers a steel rocker arm stand that locates the rocker shaft assembly and replaces the somewhat fragile stock aluminum piece.
Test 3:
We added a relatively mild LPE hydraulic roller camshaft and Comp valvesprings. Note how the cam raised the torque peak, losing a little torque below 2,800 rpm, but gaining excellent power especially above 4,000 rpm. The combination of the headers and cam was worth 21 lb-ft of torque and a whopping 65 hp peak-to-peak.
Test 4:
All we changed was to the larger LPE hydraulic roller cam, but compared to the stock baseline test, we now have picked up 100 hp!
The Difference column shows the overall loss or gain between Test 1 and Test 4
TEST 1 TEST 2 TEST 3 TEST 4 DIFF RPM TQ HP TQ HP TQ HP TQ HP TQ HP 2,000 318 120 318 121 308 118 281 108 -37 -12 2,{{{200}}} 318 134 322 136 {{{300}}} 126 261 110 -{{{57}}} -24 2,400 322 148 334 155 309 142 272 125 -50 -23 2,{{{600}}} 328 161 341 169 327 162 297 149 -31 -12 2,800 331 178 339 181 333 179 308 {{{164}}} -23 -14 3,000 330 191 342 198 336 193 325 188 - 5 - 3 3,200 333 203 343 209 342 210 337 205 + 4 +2 3,400 340 220 341 221 338 221 337 219 - 3 - 1 3,600 336 232 347 239 340 233 339 233 +3 +1 3,800 340 246 351 255 347 252 337 244 - 3 - 2 4,000 345 263 355 272 352 268 335 255 -10 - 8 4,200 338 272 354 285 358 286 342 274 + 4 +2 4,400 338 284 352 295 360 303 353 297 +15 +13 4,600 335 294 349 305 365 321 365 319 +30 +25 4,800 330 303 343 314 366 337 369 338 +39 +35 5,000 324 309 335 320 363 346 368 353 +44 +44 5,{{{200}}} 316 313 324 322 360 357 365 363 +49 +50 5,400 302 311 314 {{{323}}} 356 366 361 371 +59 +60 5,{{{600}}} 288 306 - - 348 372 356 379 +68 +73 5,800 271 {{{300}}} - - 340 376 348 385 +77 +85 6,000 257 294 - - 330 378 349 401 +92 +107 6,200 - - - - 318 376 345 409 - - 6,400 - - - - 305 374 337 411 - - 6,600 - - - - - - 329 413 - - 6,800 - - - - - - 314 408 - - Peak